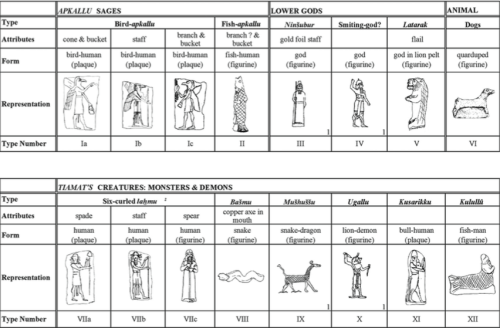
Melvin: Divine or Semi-Divine Intermediaries
The Divine Source of Civilization in Mesopotamian Myths
“The motif of the divine origin of civilization is common in the ancient Near East, especially in Mesopotamia, and it stands in stark contrast to the portrayal of the rise of civilization in Genesis 1– 11.
(Although many of my observations with regard to the view of the rise of civilization presented in Mesopotamian mythology could also be made within the mythic traditions of other ancient cultures (e.g., Egypt, Greece, Canaan), Bernard Batto notes, “[f]or reasons not entirely clear to us the opening chapters of Genesis are typologically and content-wise more akin to the mythic traditions of Mesopotamia than of territorially closer Canaan—the reverse of the normal situation in the Hebrew Bible.”
(Bernard Batto, “Creation Theology in Genesis,” R. J. Clifford and J. J. Collins [eds.], Creation in the Biblical Traditions [CBQMS, 24; Washington, D.C.: The Catholic Biblical Association of America, 1992], 16).
For this reason, as well as the general consensus that the compilation of Genesis 1–11 occurred in the exilic or early post-exilic period, in large measure as a polemic against the Babylonian cosmological worldview in which the Jewish community found itself immersed, I have limited my comparisons of the biblical material to a number of Mesopotamian myths.)
In a number of mythological texts, civilization is portrayed as a gift bestowed upon humanity by the gods, and human advancement is generally a positive development. Often the arts of civilization come to humanity through divine or semi-divine intermediaries, such as the apkallus or heroes who are either semi-divine (e.g., Gilgamesh) or divinized humans (e.g., Lugalbanda, Utnapishtim).

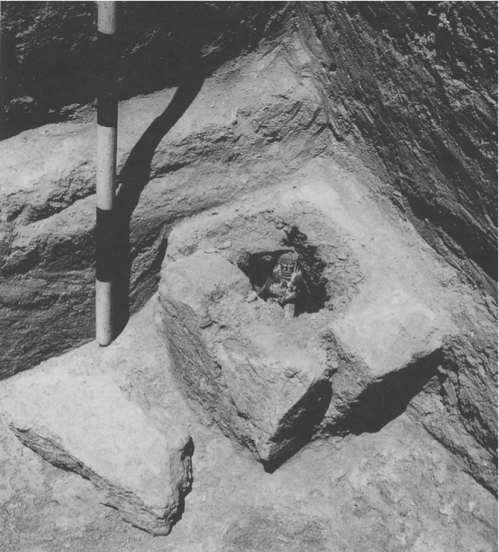
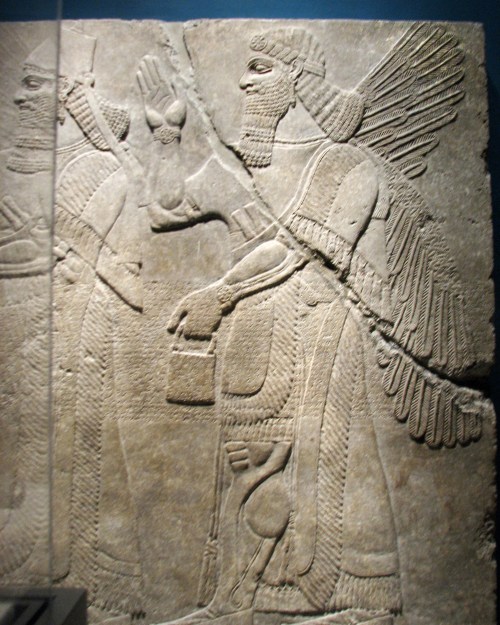
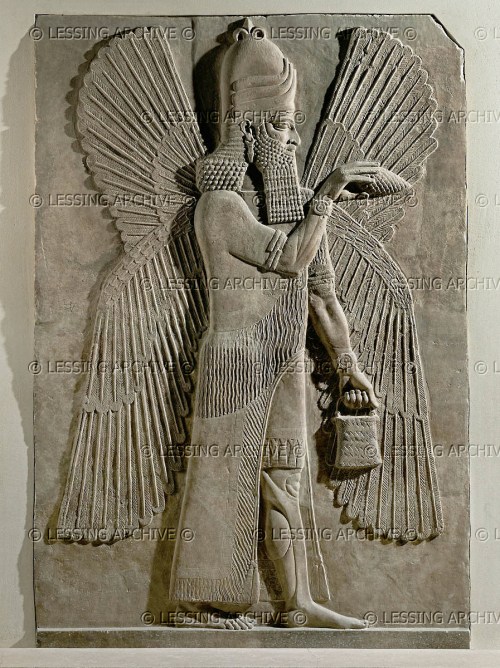
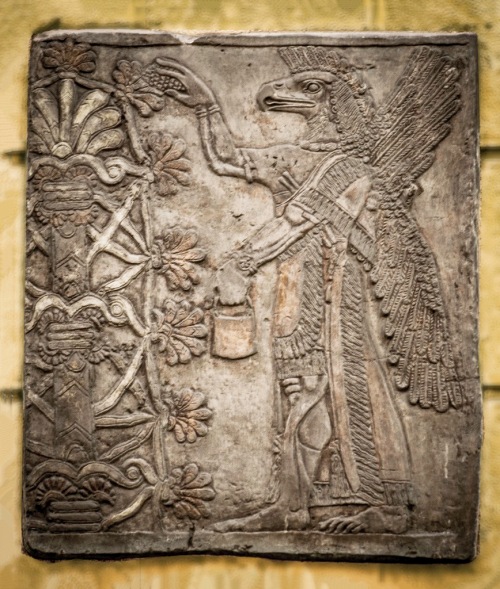
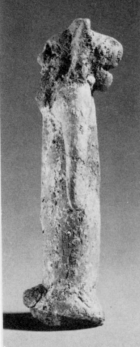
This depiction of a fish-apkallū of the purādu-fish type guarded the entrance to the temple of Ninurta at Nimrud.
A fish’s head can be seen on the Apkallu’s head, and its skin hangs down over the back of his body.
It is important to recall that the so-called Seven Sages of Sumeria were apkallū of this type.
Neo-Assyrian era, 865-860 BCE.
From the Temple of Ninurta, Nimrud (ancient Kalhu; Biblical Calah), northern Mesopotamia, Iraq. (The British Museum, London).
Osama Shukir Muhammed Amin FRCP (Glasg)
http://www.ancient.eu/image/2708/
According to the apkallu tradition, which comes to us from a wide array of sources ranging from the bilingual (Sumerian-Akkadian), “Etiological Myth of the Seven Sages” in the Bīt Mēseri texts to the much later writings of Berossus (4th century BCE) and the Uruk Sage List (c. 165 BCE), as well as the Adapa myth and the epic myth Erra and Ishum, semi-divine beings sent by Enki / Ea instructed antediluvian humans in the arts of civilization. The apkallus were teachers of early humanity whom Ea had endowed with “broad understanding” (uzna rapašta).
(Erica Reiner, “The Etiological Myth of the ‘Seven Sages,’” Orientalia 30 (1960), 4. See also Alan Lenzi, Secrecy and the Gods: Secret Knowledge in Ancient Mesopotamia and Biblical Israel (SAAS, 19; Helsinki: The Neo-Assyrian Text Corpus Project, 2008), 106–20. A similar description of the apkallus appears in the myth Erra and Ishum (COS 1.113:408).
(See the detailed description of the apkallus in Jean Bottéro, Mesopotamia: Writing, Reasoning, and the Gods (trans. Zainab Bahrani and Marc Van De Mieroop; Chicago: University of Chicago Press, 1992), 246–49. For a discussion of the Uruk Sage List, see Lenzi, Secrecy and the Gods, 106–09.)
(See Helge S. Kvanvig, Roots of Apocalyptic: The Mesopotamian Background of the Enoch Figure and the Son of Man (WMANT, 61; Neukirchen-Vluyn: Neukirchener Verlag), 295–318; Paul D. Hanson, “Rebellion in Heaven, Azazel, and Euhemeristic Heroes in 1 Enoch 6–11,” JBL 96 (1977), 226– 29.)
According to Berossus, they taught the people of Sumer “writing, science, and technology of all types, the foundation of cities, the building of temples, jurisprudence and geometry,” as well as such necessities as agriculture. In lists, they usually appear paired with the king whom they purportedly advised as a sort of vizier.”
David P. Melvin, “Divine Mediation and the Rise of Civilization in Mesopotamian Literature and in Genesis 1-11,” Journal of Hebrew Scriptures, 2010, pp. 3-4.
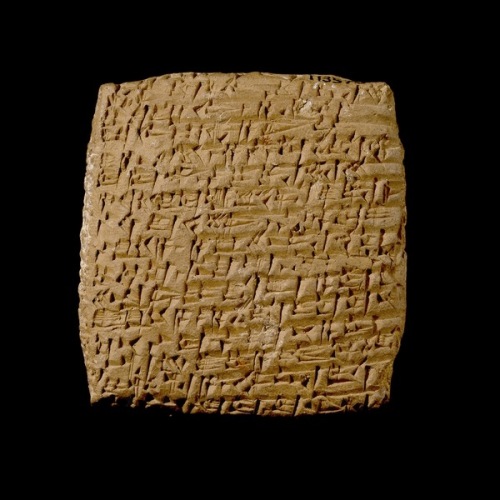









![AM-102 ; No. #1 (K4023) British Museum of London
Tablet K.4023 COL. I [Starting on Line 38] . . . Root of caper which (is) on a grave, root of thorn (acacia) which (is) on a grave, right horn of an ox, left horn of a kid, seed of tamarisk, seed of laurel, Cannabis, seven drugs for a bandage against the Hand of a Ghost thou shalt bind on his temples. FOOTNOTES: [1] - The American Journal of Semitic Languages and Literatures, Vol. 54, No. 1/4 (Oct., 1937), pp. 12-40; Assyrian Prescriptions for the Head By R. Campbell Thompson
http://antiquecannabisbook.com/chap2B/Assyria/K4023.htm](https://therealsamizdat.com/wp-content/uploads/2015/07/k4023-antdiluvian-medical-text.jpg?w=500)