Selz: An Excerpt from the Book of Giants
“The following excerpts of the reconstructed Book of Giants are taken from the edition of The Gnostic Society Library ([14 March 2010]) (MSS: 4Q203, 1Q23, 2Q26, 4Q530–532, 6Q8). This excerpt is from footnote 20 of Selz, “Of Heroes and Sages,” synopsized as Selz: On Giants.
The wicked angels, bringing both knowledge and havoc.
2 […] they knew the secrets of […] 3 [… si]n was great in the earth […] 4 […]
and they killed many […] 5 [… they begat] giants […] (1Q23 9+14+15)
The outcome of the demonic corruption was violence, perversion, and a brood of monstrous beings.
1 […] they defiled […] 2 [… they begot] giants and monsters […] 3 […] they begot, and, behold, all [the earth was corrupted . . . ] 4 [ . . . ] with its blood and by the hand of[…] 5 [giant’s ]which did not suffice for them and[…]6[…]and they were seeking to devour many [. . .] 7 [. . .] 8 [. . .] the monsters attacked it. (4Q531 2)

This is a photograph of the Great Isaiah Scroll, from the biblical scrolls recovered from Qumran.
It contains the entire known Book of Isaiah in Hebrew, probably written by an Essene scribe circa 2d century BCE.
The Israel Museum. Photo by Ardon Bar Hama. The original author, and the identity of the scribe, is not known.
This work is in the public domain in the US and those countries where a copyright term of 100 years plus the life of the author prevails.
The giants became troubled by a series of dreams and visions. Mahway sees a tablet being immersed in water. When it emerges, all but three names have been washed away. The dream evidently symbolizes the destruction of all but Noah and his sons by the Flood. . . . The giants realize the futility of fighting against the forces of heaven. The first speaker may be Gilgamesh.
3 [… I am a] giant, and by the mighty strength of my arm and my own great strength 4 [ . . . any]one mortal, and I have made war against them; but I am not [ . . . ] able to stand against them, for my opponents 6 [ . . . ] reside in [Heav]en, and they dwell in the holy places.
And not 7 [. . . they] are stronger than I. 8 [. . .] of the wild beast has come, and the wild man they call [me]. 9 [ . . . ] Then Ohya said to him, I have been forced to have a dream [ . . . ] the sleep of my eyes [vanished], to let me see a vision. Now I know that on [. . .] 11–12[. . .] Gilgamesh [. . .] (4Q531 1)
[From] Ohya’s dream vision . . .
1 concerns the death of our souls [ . . . ] and all his comrades, [and Oh]ya told them what Gilgamesh said to him 2[. . .] and it was said [. . .] “concerning [. . .] the leader has cursed the potentates” 3 and the giants were glad at his words. Then he turned and left [. . .] (4Q530 II)
More [ill-foreboding] dreams afflict the giants. . . . Someone suggests that Enoch be found to interpret the vision.
[ . . . to Enoch] the noted scribe, and he will interpret for us 12 the dream. Thereupon his fellow Ohya declared and said to the giants, 13 I too had a dream this night, O giants, and, behold, the Ruler of Heaven came down to earth 14 [ . . . ] and such is the end of the dream.
[Thereupon] all the giants [and monsters! grew afraid 15 and called Mahway. He came to them and the giants pleaded with him and sent him to Enoch 16 [the noted scribe].
They said to him, Go […] to you that 17 […] you have heard his voice. And he said to him, He will [. . . and] interpret the dreams [. . .] III:3 [. . .] how long the giants have to live. [. . .] (4Q530 II–III)
After a cosmic journey Mahway comes to Enoch and makes his request.
3 [ . . . he mounted up in the air] 4 like strong winds, and flew with his hands like ea[gles . . . he left behind] 5 the inhabited world and passed over Desolation, the great desert [ . . . ] 6 and Enoch saw him and hailed him, and Mahway said to him [. . .] 7 hither and thither a second time to Mahway [. . .
The giants await 8 your words, and all the monsters of the earth. If [. . .] has been carried [. . .] 9 from the days of […] their […] and they will be added […] 10 […] we would know from you their meaning [ . . . ] 11 [ . . . two hundred tr]ees that from heaven [came down . . . ] (4Q530 III)
[Then,] Enoch sends back a tablet with its grim message of judgment, but with hope for repentance.”
(With this text, compare Genesis 6:1–2, 4. See further L.T. Stuckenbruck, The Book of Giants from Qumran: Texts, Translation, and Commentary (TSAJ 63; Tübingen: Mohr Siebeck, 1997) and K. Beyer, Die aramäischen Texte vom Toten Meer: samt den Inschriften aus Palästina, dem Testament Levi aus der Kairoer Genisa, der Fastenrolle und den alten talmudischen Zitaten: Aramaistische Einleitung, Text, Übersetzung, Deutung, Grammatik/ Wörterbuch, deutsch-aramäische Wortliste, Register (2 vols. and Ergänzungsband; Göttingen: Vandenhoeck & Ruprecht, 1984/1994/2004), 1:225–258 (1 Enoch), 258–268 (Book of Giants), Ergänzungsband: 117–118 (1 Enoch), 119–124 (Book of Giants), 2:153–155 (1 Enoch), 155–162 (Book of Giants).
We note that Beyer postulates a Jewish Old Palestinian language for these earliest Enoch fragments (ibid., 1:229). He understands these fragments as an early translation from a Hebrew original. Especially important is É. Puech, Qumran Grotte 4.XXII: Textes araméns, première partie: 4Q529–549 (DJD XXXI; Oxford: Clarendon, 2001).”
Gebhard J. Selz, “Of Heroes and Sages–Considerations of the Early Mesopotamian Background of Some Enochic Traditions,” in Armin Lange, et al, The Dead Sea Scrolls in Context, v. 2, Brill, 2011, pp. 782-4.










































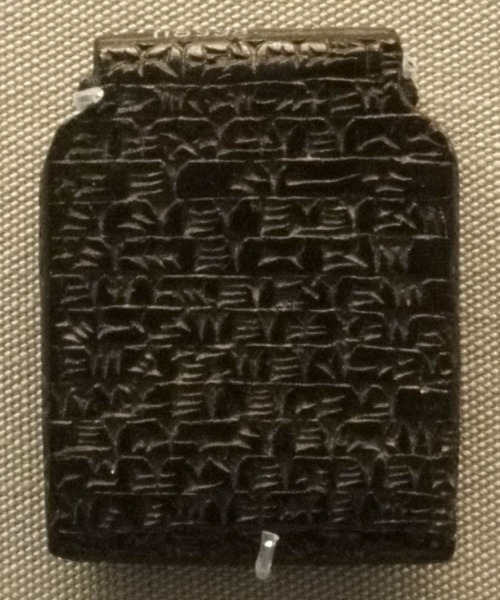
![AM-102 ; No. #1 (K4023) British Museum of London
Tablet K.4023 COL. I [Starting on Line 38] . . . Root of caper which (is) on a grave, root of thorn (acacia) which (is) on a grave, right horn of an ox, left horn of a kid, seed of tamarisk, seed of laurel, Cannabis, seven drugs for a bandage against the Hand of a Ghost thou shalt bind on his temples. FOOTNOTES: [1] - The American Journal of Semitic Languages and Literatures, Vol. 54, No. 1/4 (Oct., 1937), pp. 12-40; Assyrian Prescriptions for the Head By R. Campbell Thompson
http://antiquecannabisbook.com/chap2B/Assyria/K4023.htm](https://ma91c1an.files.wordpress.com/2015/07/k4023-antdiluvian-medical-text.jpg?w=500)
































