“During the course of the years studying and teaching the Primeval History as recorded in the literary texts of ancient Mesopotamia, this writer has been struck by certain similarities between the Akkadian apkallu (Sumerian algal / NUN.ME / EN.ME), creatures of the god Ea, the “sages of old,” and the biblical nēpīlîm of Genesis 6 who are introduced just before the flood account.
In the Mesopotamian king and sage lists, the apkallu occur in the pre-flood era, and in some texts for a limited time after the flood. In general, however, the pre-flood sages are called apkallu and their traditional number is seven, while the post-flood sages are called the ummiānu.

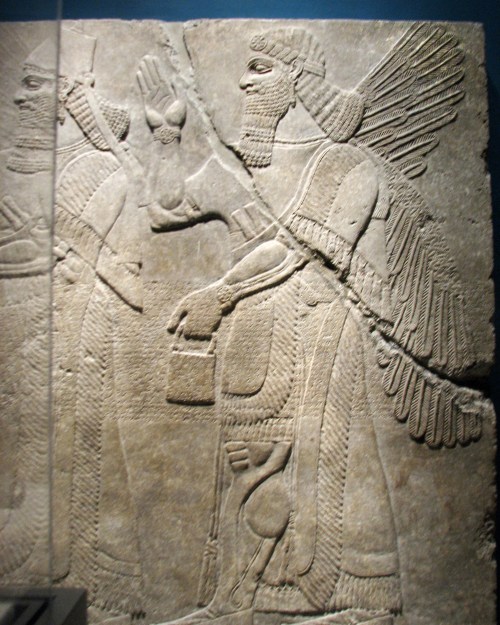
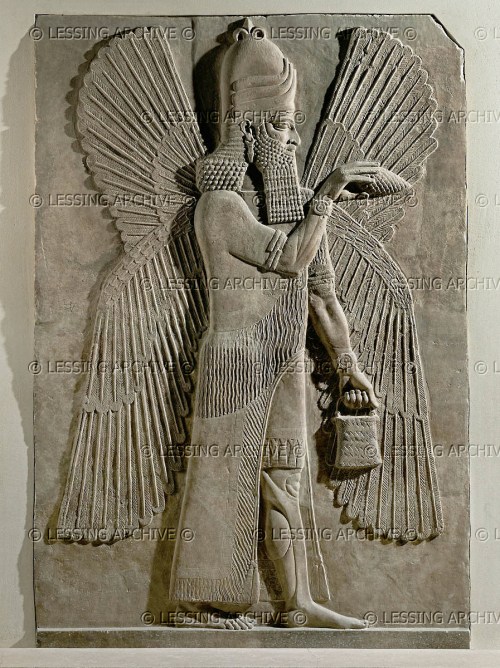
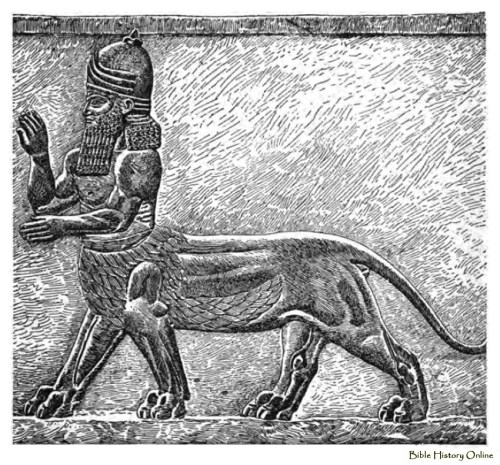
Apkallu portrayed with Ea, at far left, with water coursing from his shoulders.
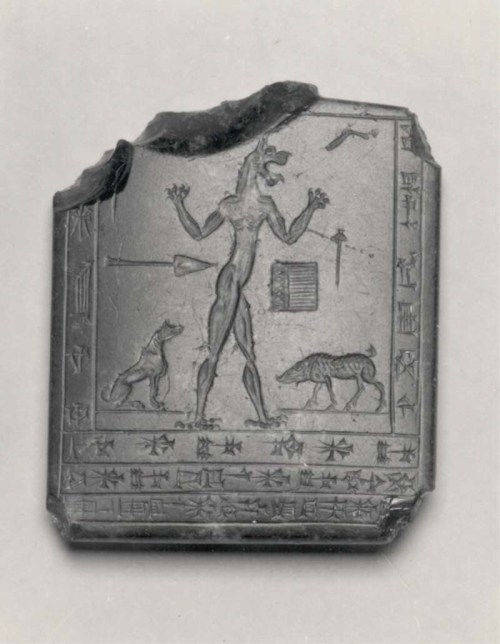
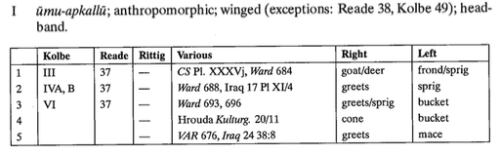
The apkallu are semi-divine beings who may be depicted as mixed beings, as priests wearing fish hoods, or who may, like Adapa, be called a son of Ea. Moreover, humans and apkallu could presumably mate since we have the description of the four post-flood apkallu as “of human descent,” the fourth being only “two-thirds apkallu” as opposed to pre-flood pure apkallu and subsequent human sages (ummiānu).

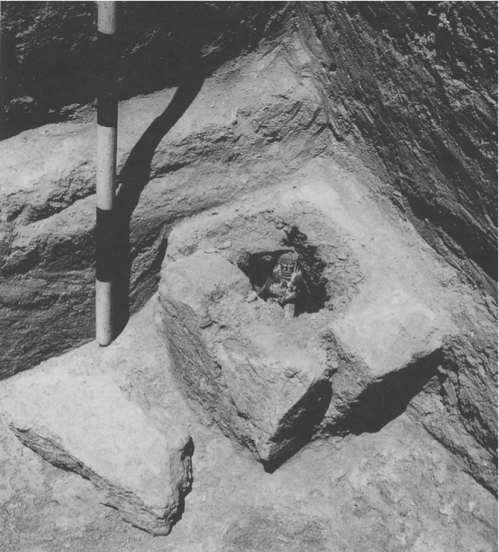
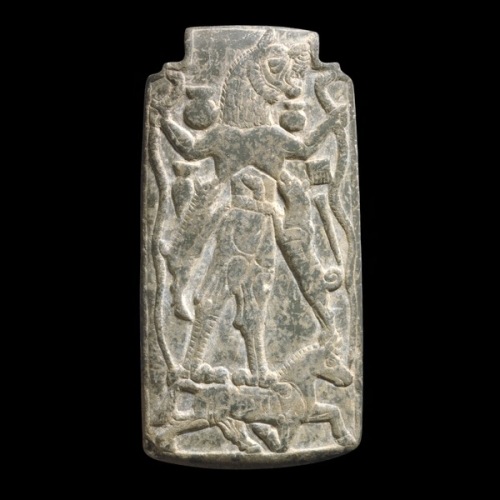
A depiction of the apkallu, Adapa, or Oannes.
The short mythological “episode” in Genesis 6:1-4 tells us only that after the population increased, the nēpīlîm appeared on the earth after divine beings (sons of elohim) had mated with the daughters of men. The following verse (v. 5) states that Yahweh saw that men’s wickedness was great.
It can be assumed from this brief account that the nēpīlîm were the offspring of those divine fathers and human mothers, and that it was the nēpīlîm who somehow exemplified wicked mankind in general. Let us now turn to the Mesopotamian apkallu tales and lists to see how their behavior, as well as their parentage, may have some features in common with the nēpīlîm.

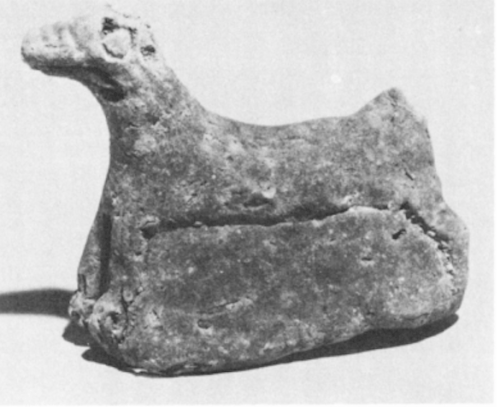
Antediluvian apkallu portrayed as fish-men, such mixed-species creatures were the teachers of men.
The most celebrated apkallu was Adapa, identified as a son of Ea. As we are told in the best known and best preserved myth about him, he executed an act of hubris by breaking the wing of the south wind; the end result, for him, of that wicked act was that he was denied immortality.
He is probably to be equated with the last antediluvian apkallu who was reported to have ascended to heaven. As we know from the late lists of sages, several other apkallu at the time of the flood or right after it also committed daring or wicked acts (the list that follows is abbreviated with respect to details and is conflated from the pertinent texts):
Antediluvian apkallu
- Uanna — Who completed the plans of heaven and earth
- Uannedugga — Who was endowed with comprehensive intelligence
- Enmedugga — Who was allowed a good fate
- Enmegaluamma — Who was born in a house
- Enmebulugga — Who grew up on pasture land
- Anenlilda — The exorcist of Eridu
- Utuabzu (Utuabba) — Who ascended to heaven
- [Total of] seven brilliant purādu fish . . . born in the river, who direct the plans of heaven and earth.
(Editorial note, source: Bit Mēseri III, 14’=27′)
Postdiluvian apkallu
- (both Adapa and Nunpiriggaldim are associated with Enmerkir)
- Nungalpiriggaldim — Who brought down Ishtar from heaven and who made the harp decorated with bronze and lapis*
- Piriggalnungal — Who angered Adad*
- Piriggalabsu — Who angered Ea*
- Lu-Nanna (2/3d apkallu) — Who drove the dragon from Ishtar’s temple*
- *[Total of] four of human descent whom (pl.) Ea endowed with comprehensive intelligence.
(Editorial note, also see source: Helge Kvanvig, Traditions of the Apkallus, Primeval History: Babylonian, Biblical and Enochic: An Intertextual Reading, Brill, 2011.)
Thus we see that the traditions about the superhuman apkallu contained stories, most of them lost to us, about their famous and infamous deeds. But it is the latter ones, from Adapa to Piriggalabzu (sic), around whom the obvious misbehavior clusters.
It is of further interest to note that the pivotal role of the nēpīlîm passage in Genesis 6 occurs together with the theme of increased population growth on which Genesis 6 opens. If we compare the Mesopotamian material, we see a similar position in the storytelling for the importance of population increase and concomitant wickedness as a factor leading to the flood.
The Mesopotamian sages were endowed with wisdom and special powers because they were created by the god Ea and associated with the deep (as fish-men, etc.). Because of their powers they were capable of acts that could impress or offend the gods, that could cause beneficial or harmful natural phenomena.
It is the negative side of them that seems to be involved in the period just before and after the flood in the sage lists. A similar theme runs through the Atrahasis Epic; there, at each attempt of the gods to decrease men’s numbers by means of drought, etc., Ea instructs his son (?) Atrahasis, the Extra Wise and thus a sage figure in his own right but also to be equated with the king of Shuruppak, how to outwit the gods and overcome hardship.
Thus each god whose cult is neglected and deprived of offerings, as a result of those instructions, was sure to be angered. Their collective anger at such acts and their disgust at humanity’s increase and bad condition led to the joint decision to send the flood.
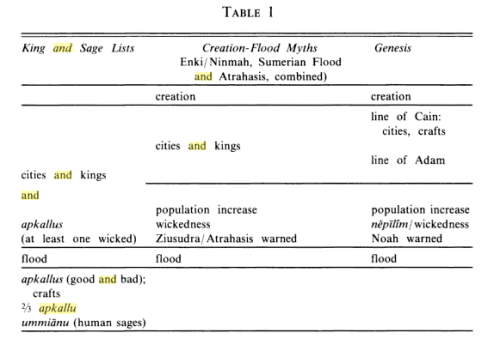
Whereas the Mesopotamian myth and list traditions single out and keep distinct the sages and king-heroes, Genesis 6:4 speaks only of the “heroes of old, men of renown” and equates them with the nēpīlîm. In fact, it is possible that this verse intended to equate both the lines of Adam and Cain with the nēpīlîm. If so, the reintroduction of Noah four verses later would complete the line of thinking, since Noah was one of the heroes of old.
Yet the line of Cain (the Smith), juxtaposed as it is with the line of Adam, seems to operate in a manner similar to the Mesopotamian traditional list of the line of sages juxtaposed with the line of kings, as others have argued.
Like the apkallu who built the early cities and those who brought the civilized arts to men, the line of Cain performed the same service (or dis-service, in the biblical view). As to v 3 concerning man’s shortened lifespan, it may have its counterpart in the post-flood renegotiations of the terms for man’s continued existence as described in the Atrahasis Epic.
There, the fixing of a term of life for mortals was probably contained in the fragmentary section about controlling population growth. In the Sumerian King List it is only after King Gilgamesh (who was 1/3d divine) that rulers begin to have more normal longevity (beginning with the 126 year reign of his successor).

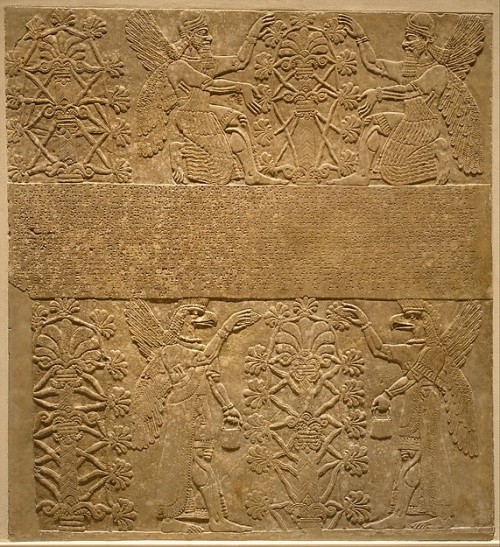
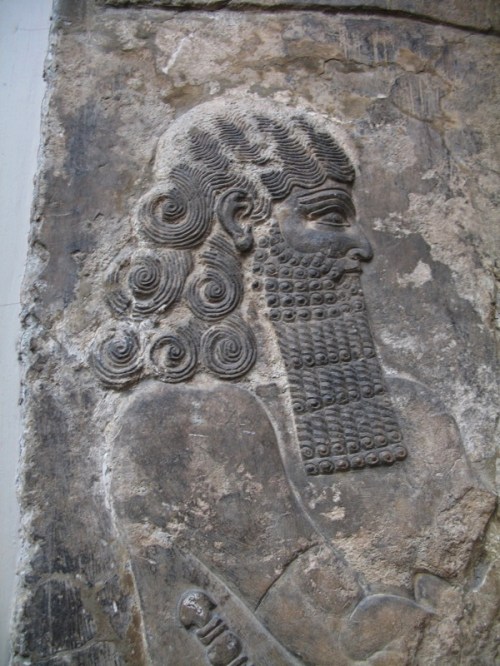
Postdiluvian advisors to kings who were men, the ummianu, were the successors of the antediluvian mixed-species Apkallu who were portrayed as fish-men. In this frieze now held in the British Museum they tend to a sacred tree. The antediluvian Apkallu were the so-called seven sages of Sumeria.
One other cuneiform text can be mentioned in which the sages may be associated with wicked acts, viz. The Epic of Erra (alternative full text of the Epic from Foster’s B is available). There the sages (called ummiānu) seem to be guilty by implication since we are told that they were dispatched for good to the apsu at the time of the flood and may have been deprived access to the mes-tree, “the flesh of the gods,” which provided them with the special material to make divine and kingly statues (as well as knowledge, skill and longevity?), but which was hidden from them (and all future mortals) forever when Marduk cast it into the deep.
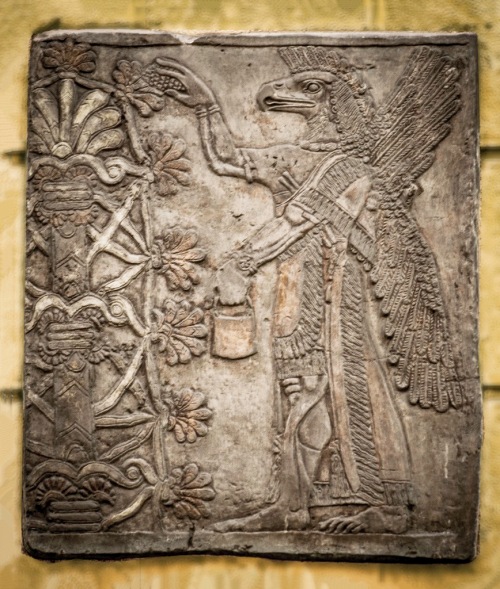

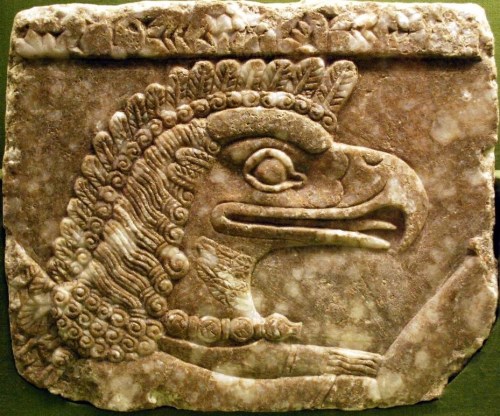
In Neo-Assyrian art these bird-headed “genies,” as they are often described, are now known to be apkallu, mixed-feature creatures created by the god Ea. They traditionally served as advisors to kings. They are often depicted in association with sacred trees.
https://www.flickr.com/photos/lanpernas2/8606000868/
If the flood is the same Abubu perhaps the mes-tree (see footnote 11 below) may be compared with the plant (of life) whose hidden location in the deep Utnapishtim revealed to Gilgamesh. If so, it leads us to suspect a further connection between the Mesopotamian mythological trees and plants and the tree(s) in Eden to which another sage figure, Adam, had once had access.

A modern depiction of Gilgamesh harvesting the Plant of Life from the ocean floor, guided by Utnapishtim, the deified survivor of the Deluge.
http://www.mediahex.com/Utnapishtim
In short, we may be able to look to the Mesopotamian sage traditions for the mythological background of Genesis 6:1-4. While the ties between the apkallu and the nēpīlîm are hardly ties that bind, there are enough points of comparison—superhuman / semi-divine beings, acts of daring / hubris, acts that anger divinity, association with wickedness in men, their predominantly pre-flood existence—to encourage our consideration.
The Mischwesen sages seem at least to be closer to the nēpīlîm topically than the theogony materials concerning the generations of the gods. It is hoped that the circumstantial evidence for a remote connection between the apkallu and the nēpīlîm is strong enough to have been worth trying the case.”
(Footnote 11: Now that the bird-faced winged genies of Assyrian Palace art may be identified as apkallu (see Anthony Green, “Neo-Assyrian Apotropaic Figures,” Iraq 45 (1983), pp. 87-96) the close association of apkallu with special trees is clear.)
(For other mixed-beings, creatures of Ea, note F. Köcher, “Der babylonische Göttertypentext,” Mitteilungen des Instituts für Orientforschung 1 (1953), pp. 72, 74, 78, 80.)
Anne Draffkorn Kilmer, “The Mesopotamian Counterparts of the Biblical Nephilim,” in Francis I. Andersen, Edgar W. Conrad, & Edward G. Newing, eds., Perspectives on Language and Text: Essays and Poems in Honor of Francis I. Andersen’s Sixtieth Birthday, 1985, pp. 39-43.