“The god Osiris, as we have seen in the chapter on the Egyptian Religion in the accompanying volume, lived and reigned at one time upon earth in the form of a man. His twin-brother Set was jealous of his popularity, and hated him to such a degree that he contrived a plan whereby he succeeded in putting Osiris to death.
Set then tried to usurp his brother’s kingdom and to make himself sole lord of Egypt, and, although no text states it distinctly, it is clear that he seized his brother’s wife, Isis, and shut her up in his house.
Isis was, however, under the protection of the god Thoth, and she escaped with her unborn child, and the following Legend describes the incidents that befell her, and the death and revivification of Horus.
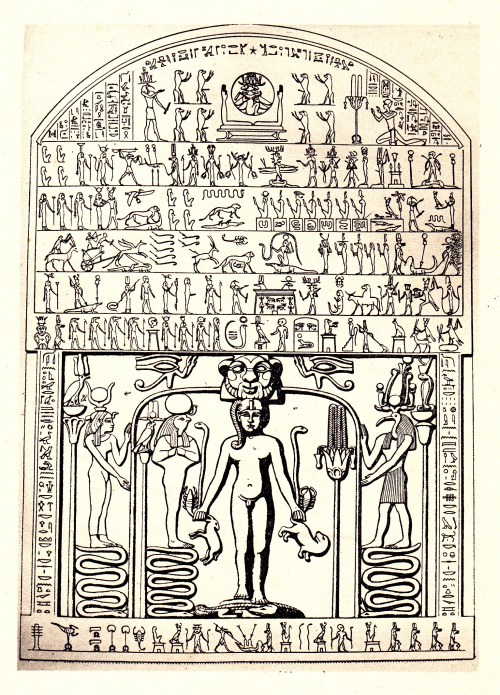
It is cut in hieroglyphs upon a large stone stele which was made for Ankh-Psemthek, a prophet of Nebun in the reign of Nectanebus I, who reigned from 373 B.C. to 360 B.C. The stele was dug up in 1828 at Alexandria, and was given to Prince Metternich by Muhammad Ali Pasha; it is now commonly known as the “Metternich Stele.”
The Legend is narrated by the goddess herself, who says:
“I am Isis. I escaped from the dwelling wherein my brother Set placed me. Thoth, the great god, the Prince of Truth in heaven and on earth, said unto me:
“Come, O goddess Isis [hearken thou], it is a good thing to hearken, for he who is guided by another liveth. Hide thyself with thy child, and these things shall happen unto him. His body shall grow and flourish, and strength of every kind shall be in him. He shall sit upon his father’s throne, he shall avenge him, and he shall hold the exalted position of ‘Governor of the Two Lands.’”
I left the house of Set in the evening, and there accompanied me Seven Scorpions, that were to travel with me, and sting with their stings on my behalf. Two of them, Tefen and Befen, followed behind me, two of them, Mestet and Mestetef, went one on each side of me, and three, Petet, Thetet, and Maatet, prepared the way for me.
I charged them very carefully and adjured them to make no acquaintance with any one, to speak to none of the Red Fiends, to pay no heed to a servant (?), and to keep their gaze towards the ground so that they might show me the way.
And their leader brought me to Pa-Sui, the town of the Sacred Sandals, [These places were in the seventh nome of Lower Egypt (Metelites)] at the head of the district of the Papyrus Swamps. When I arrived at Teb I came to a quarter of the town where women dwelt.
And a certain woman of quality spied me as I was journeying along the road, and she shut her door in my face, for she was afraid because of the Seven Scorpions that were with me. Then they took counsel concerning her, and they shot out their poison on the tail of Tefen. As for me, a peasant woman called Taha opened her door, and I went into the house of this humble woman.
Then the scorpion Tefen crawled in under the door of the woman Usert [who had shut it in my face], and stung her son, and a fire broke out in it; there was no water to put it out, but the sky sent down rain, though it was not the time of rain. And the heart of Usert was sore within her, and she was very sad, for she knew not whether her son would live or die; and she went through the town shrieking for help, but none came out at the sound of her voice.
And I was sad for the child’s sake, and I wished the innocent one to live again. So I cried out to her, saying, Come to me! Come to me! There is life in my mouth. I am a woman well known in her town. I can destroy the devil of death by a spell which my father taught me. I am his daughter, his beloved one.
Then Isis laid her hands on the child and recited this spell:
“O poison of Tefent (sic), come forth, fall on the ground; go no further. O poison of Befent (sic), come forth, fall on the ground. I am Isis, the goddess, the mistress of words of power. I am a weaver of spells, I know how to utter words so that they take effect. Hearken to me, O every reptile that biteth (or stingeth), and fall on the ground. O poison of Mestet, go no further. O poison of Mestetef, rise not up in his body. O poison of Petet and Thetet, enter not his body. O poison of Maatet, fall on the ground.
Ascend not into heaven, I command you by the beloved of Ra, the egg of the goose which appeareth from the sycamore. My words indeed rule to the uttermost limit of the night. I speak to you, O scorpions. I am alone and in sorrow, and our names will stink throughout the nomes….
The child shall live! The poison shall die! For Ra liveth and the poison dieth. Horus shall be saved through his mother Isis, and he who is stricken shall likewise be saved.”
Meanwhile the fire in the house of Usert was extinguished, and heaven was content with the utterance of Isis. Then the lady Usert was filled with sorrow because she had shut her door in the face of Isis, and she brought to the house of the peasant woman gifts for the goddess, whom she had apparently not recognized.
The spells of the goddess produced, of course, the desired effect on the poison, and we may assume that the life of the child was restored to him. The second lot of gifts made to Isis represented his mother’s gratitude.
Exactly when and how Isis made her way to a hiding place cannot be said, but she reached it in safety, and her son Horus was born there.
The story of the death of Horus she tells in the following words:
“I am Isis. I conceived a child, Horus, and I brought him forth in a cluster of papyrus plants (or, bulrushes). I rejoiced exceedingly, for in him I saw one who would make answer for his father. I hid him, and I covered him up carefully, being afraid of that foul one [Set], and then I went to the town of Am, where the people gave thanks for me because they knew I could cause them trouble.
I passed the day in collecting food for the child, and when I returned and took Horus into my arms, I found him, Horus, the beautiful one of gold, the boy, the child, lifeless! He had bedewed the ground with the water of his eye and with the foam of his lips. His body was motionless, his heart did not beat, and his muscles were relaxed.”
Then Isis sent forth a bitter cry, and lamented loudly her misfortune, for now that Horus was dead she had none to protect her, or to take vengeance on Set. When the people heard her voice they went out to her, and they bewailed with her the greatness of her affliction. But though all lamented on her behalf there was none who could bring back Horus to life.
Then a “woman who was well known in her town, a lady who was the mistress of property in her own right,” went out to Isis, and consoled her, and assured her that the child should live through his mother.
And she said, “A scorpion hath stung him, the reptile Aunab hath wounded him.” Then Isis bent her face over the child to find out if he breathed, and she examined the wound, and found that there was poison in it, and then taking him in her arms, “she leaped about with him like a fish that is put upon hot coals,” uttering loud cries of lamentation.
During this outburst of grief the goddess Nephthys, her sister, arrived, and she too lamented and cried bitterly over her sister’s loss; with her came the Scorpion-goddess Serqet.
Nephthys at once advised Isis to cry out for help to Ra, for, said she, it is wholly impossible for the Boat of Ra to travel across the sky whilst Horus is lying dead.
Then Isis cried out, and made supplication to the Boat of Millions of Years, and the Sun-god stopped the Boat. Out of it came down Thoth, who was provided with powerful spells, and, going to Isis, he inquired concerning her trouble.
“What is it, what is it, O Isis, thou goddess of spells, whose mouth hath skill to utter them with supreme effect? Surely no evil thing hath befallen Horus, for the Boat of Ra hath him under its protection. I have come from the Boat of the Disk to heal Horus.”
Then Thoth told Isis not to fear, but to put away all anxiety from her heart, for he had come to heal her child, and he told her that Horus was fully protected because he was the Dweller in his disk, and the firstborn son of heaven, and the Great Dwarf, and the Mighty Ram, and the Great Hawk, and the Holy Beetle, and the Hidden Body, and the Governor of the Other World, and the Holy Benu Bird, and by the spells of Isis and the names of Osiris and the weeping of his mother and brethren, and by his own name and heart.
Turning towards the child Thoth began to recite his spells and said, “Wake up, Horus! Thy protection is established. Make thou happy the heart of thy mother Isis. The words of Horus bind up hearts and he comforteth him that is in affliction. Let your hearts rejoice, O ye dwellers in the heavens. Horus who avenged his father shall make the poison to retreat.
That which is in the mouth of Ra shall circulate, and the tongue of the Great God shall overcome [opposition]. The Boat of Ra standeth still and moveth not, and the Disk (i.e. the Sun-god) is in the place where it was yesterday to heal Horus for his mother Isis.
Come to earth, draw nigh, O Boat of Ra, O ye mariners of Ra; make the boat to move and convey food of the town of Sekhem (i.e. Letopolis) hither, to heal Horus for his mother Isis….
Come to earth, O poison! I am Thoth, the firstborn son, the son of Ra. Tem and the company of the gods have commanded me to heal Horus for his mother Isis.
O Horus, O Horus, thy Ka protecteth thee, and thy Image worketh protection for thee. The poison is as the daughter of its own flame; it is destroyed because it smote the strong son. Your temples are safe, for Horus liveth for his mother.”
Then the child Horus returned to life, to the great joy of his mother, and Thoth went back to the Boat of Millions of Years, which at once proceeded on its majestic course, and all the gods from one end of heaven to the other rejoiced.
Isis entreated either Ra or Thoth that Horus might be nursed and brought up by the goddesses of the town of Pe-Tep, or Buto, in the Delta, and at once Thoth committed the child to their care, and instructed them about his future.
Horus grew up in Buto under their protection, and in due course fought a duel with Set, and vanquished him, and so avenged the wrong done to his father by Set.”
–E. A. Wallis Budge, The Literature of the Ancient Egyptians, 1914, pp. 43-5.