Oannes and the Apkallu, the Seven Sages of Sumeria
“Placed between two other books, Babyloniaca 2 takes on the function of a narrative pivot in Berossos’ work. It has connections with book one and book three, by way of recapitulation (e.g. Oannes and the sages) and anticipation (mention of kings who are treated in book three); and it brings into contact two fundamentally different periods in history: the mythic prehistory of book 1, which is cast as a revelation transmitted by the semi-divine sage Oannes; and the political history of book 3, which bears out Oannes’ revelation in a setting where gods and humans are much more clearly separate.
Book 2 of Berossos’ Babyloniaca contains, as far as we can tell, the history of Babylonian kingship organised according to a very traditional pattern. Broadly speaking, it comprises the ten kings before the Flood, the deluge narrative and a concise history of rulers down to Nabonassar.

Among all the extant exemplars of the Sumerian King List, the Weld-Blundell prism in the Ashmolean Museum cuneiform collection represents the most extensive version as well as the most complete copy of the King List. It lists rulers from the antediluvian dynasties to Suen-magir, the fourteenth ruler of the Isin dynasty (ca. 1763–1753 B.C.). The prism contains four sides with two columns on each side. Perforated, the prism must originally have a wooden spindle going through its centre so that it might be rotated and read on all four sides.
http://cdli.ox.ac.uk/wiki/doku.php?id=the_sumerian_king_list_sklid=the_sumerian_king_list_skl
The structural backbone of the book is a king list, more specifically, the so-called Sumerian King List in a version which contains sections before and after the Flood. The time before the Flood is structured by the succession of antediluvian kings, that after the Flood traces the reigns of postdiluvian kings, thus forming a narrative diptych around the central Flood narrative. Eusebius describes the overall effect as follows:
“This Berosos narrated in his first book, and in the second he wrote ordering the kings one after another… In collecting the names of the kings he collects [that] alone, but he tells nothing precise of their deeds, indeed he did not consider them worthy of mention […].”
Eusebius’ complaint notwithstanding, Berossos does seem to have fleshed out the skeleton of his king list with some narrative interludes. For example, he inserts references to the antediluvian sages, a peculiarity paralleled in cuneiform sources of the Hellenistic period.
The combination of the list itself and the Flood narrative continued unchanged down to the first millennium BCE and is also attested in some fragments from the Neo-Assyrian and Late Babylonian period.
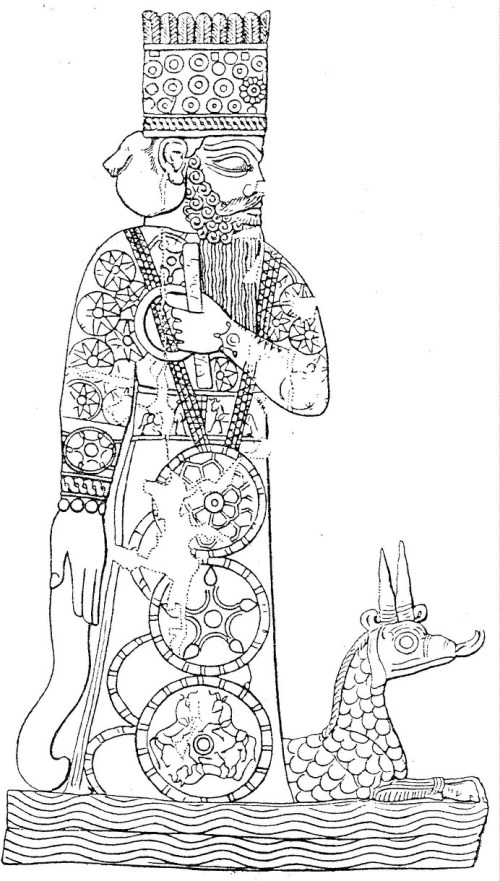
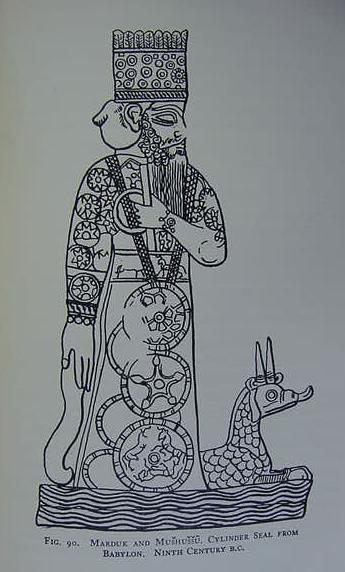
More specifically, Berossos connects the beginnings of humanity with the Oannes theme from book one. As far as we can tell, that theme appeared twice in the Babyloniaca: near the beginning of the work, Berossos introduces Oannes as the ‘paragon of Mesopotamian scholarly mysticism and wisdom’.
‘In the very first year’, a fearsome beast named Oannes appears out of the Red Sea and teaches humankind the arts of civilisation. In book 2, we learn that he is only the first in a series of other such beasts (F3a).

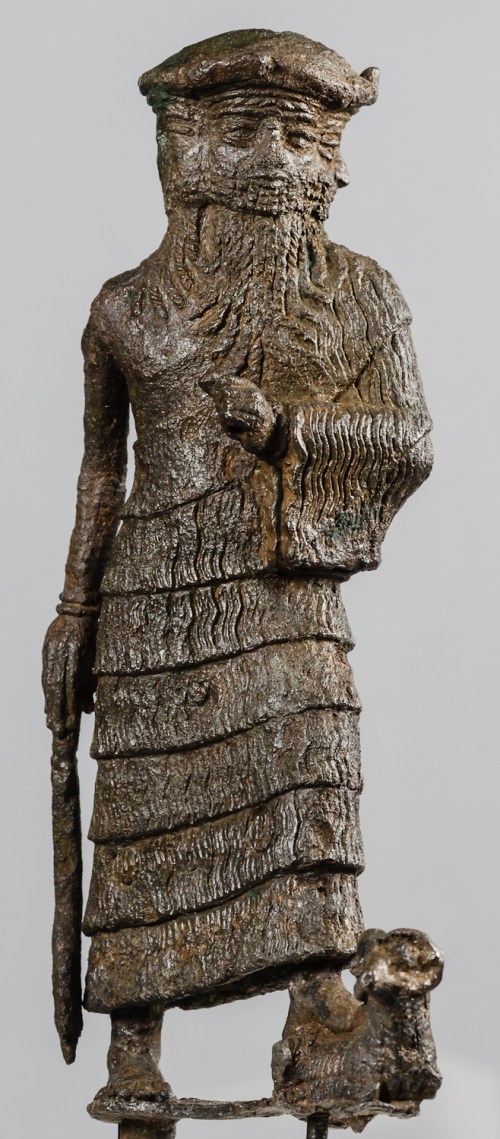
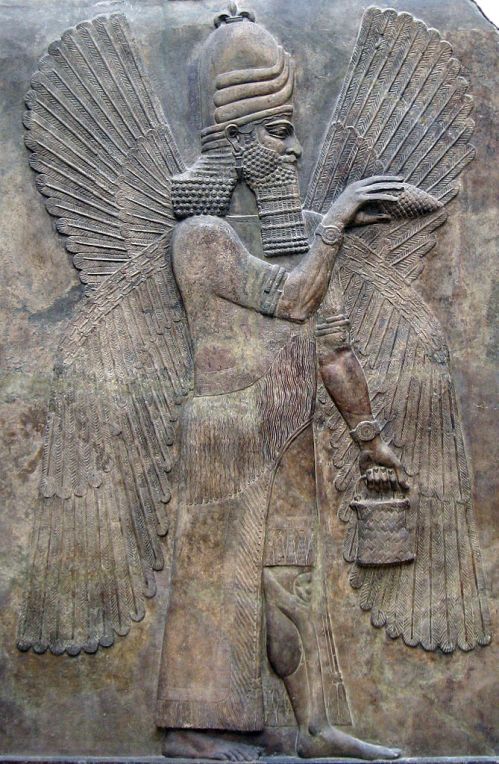
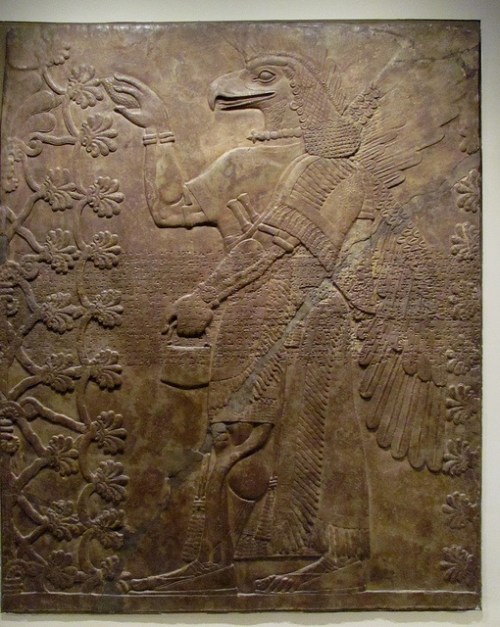
This protective spirit (Apkallu or Abkallu) guarded the entrance to the temple of Ninurta at Nimrud. A fish’s head can be seen on Apkallu’s head, and its skin hangs down over the back of Apkallu’s body.
Neo-Assyrian era, 865-860 BCE. From the Temple of Ninurta, Nimrud (ancient Kalhu; Biblical Calah), northern Mesopotamia, Iraq. (The British Museum, London).
Osama Shukir Muhammed Amin FRCP (Glasg)
http://www.ancient.eu/image/2708/
Oannes, however, is clearly the most important: he is depicted as more than a mere culture hero but acts as something very close to a creator god himself, shaping amorphous matter and turning mindless creatures into human beings with an identity and creative intelligence.
Oannes alone is responsible for the growth of human civilisation and its manifestations in history. Moreover, in describing his intervention, Berossos combines what in Sumero-Akkadian tradition were known as divine acts of creation with the teachings that humanity traditionally attributed to the apkallu, the mysterious seven sages who were created and inspired by Enki/Ea, the god of wisdom.
Part of the reason here, I suspect, might be that Berossos tried to make Oannes more plausible to a Greek audience by giving him some of the attributes of the Platonic δημιουργός (dēmiurgós), who acts ‘like a versatile artist or craftsman, creates his work from available materials according to a predetermined plan (PI. Resp. 507c; 530 a; 597b ff.; PI. Soph. 265c ff.; PI. Pit. 269c ff.; 272e ff.; PI. 7V.)’.
The aim is to underline the enormous age of Babylonian culture, the beginnings of which coincide with the dawn of all human culture. It is significant therefore that Berossos recapitulates the Oannes theme when he finally starts his account of human history in Babyloniaca 2.”
Martin Lang, “Book Two: Mesopotamian Early History and the Flood Story,” from Johannes Haubold, Giovanni B. Lanfranchi, Robert Rollinger, John Steele (eds.), The World of Berossos, Proceedings of the 4th International Colloquium on the Ancient Near East Between Classical and Ancient Oriental Traditions, Harrassowitz Verlag, Wiesbaden, 2013, pp. 48-9.








![From left, Storm God Ninurta, with bows and arrows. Ishtar, queen of heaven and earth is elevated with wings and spears and maces on her shoulders. The tree of life sprouts to her right, our left. The Sun God Shamash rises from the mountain Kur in the center, with rays of light on his shoulder. The God of Water and Wisdom, Enki/Ea battles the bird-god Imdugud/Anzu, with depictions of the Tigris and Euphrates rivers and fish coursing from his shoulders. At far right is the deified vizier Usmu, the two-faced. All gods wear conical hats with four pairs of horns. At far left is the word Adda in Accadian cuneiform, "Scribe." Accordingly this cylinder seal is known as the Seal of Adda, Akkadian period, 2350-2100 BCE. British Library. [No. 89,115.] http://www.ancientworlds.net/aw/Article/787375](https://therealsamizdat.com/wp-content/uploads/2015/05/00099452_000.jpg?w=500)












![Assyrian star map from Nineveh (K 8538). Counterclockwise from bottom: Sirius (Arrow), Pegasus + Andromeda (Field + Plough), [Aries], the Pleiades, Gemini, Hydra + Corvus + Virgo, Libra. Drawing by L.W.King with corrections by J.Koch. Neue Untersuchungen zur Topographie des Babilonischen Fixsternhimmels (Wiesbaden 1989), p. 56ff. http://doormann.tripod.com/asssky.htm](https://therealsamizdat.com/wp-content/uploads/2015/04/assyrian-star-map-from-nineveh.jpg?w=500)