Lenzi: The Antediluvian Medical Tablet from Ashurbanipal’s Library (K.4023)
“As is well-known, antediluvian knowledge had special significance in Mesopotamia. (For other examples of antediluvian knowledge (though sometimes in a broken context), see the examples gathered by Lambert, “Catalogue of Texts and Authors,” 72 at the note on VI 15.)
The most important example of this fact for the purposes of this study comes from an oft cited colophon of a medical tablet from Ashurbanipal’s library, AMT 105,1 (K.4023), lines 21-25.
![AM-102 ; No. #1 (K4023) British Museum of London
Tablet K.4023 COL. I [Starting on Line 38] . . . Root of caper which (is) on a grave, root of thorn (acacia) which (is) on a grave, right horn of an ox, left horn of a kid, seed of tamarisk, seed of laurel, Cannabis, seven drugs for a bandage against the Hand of a Ghost thou shalt bind on his temples. FOOTNOTES: [1] - The American Journal of Semitic Languages and Literatures, Vol. 54, No. 1/4 (Oct., 1937), pp. 12-40; Assyrian Prescriptions for the Head By R. Campbell Thompson
http://antiquecannabisbook.com/chap2B/Assyria/K4023.htm](https://therealsamizdat.com/wp-content/uploads/2015/07/k4023-antdiluvian-medical-text.jpg?w=500)
AM-102 ; No. #1 (K4023)
British Museum of London
Tablet K.4023
COL. I
[Starting on Line 38] . . .
Root of caper which (is) on a grave, root of thorn (acacia) which (is) on a grave, right horn of an ox, left horn of a kid, seed of tamarisk, seed of laurel, Cannabis, seven drugs for a bandage against the Hand of a Ghost thou shalt bind on his temples.
FOOTNOTES:
[1] – The American Journal of Semitic Languages and Literatures, Vol. 54, No. 1/4 (Oct., 1937), pp. 12-40; Assyrian Prescriptions for the Head By R. Campbell Thompson
http://antiquecannabisbook.com/chap2B/Assyria/K4023.htm
This colophon shows not only the association of antediluvian sages and a human sage but also the “mythology of scribal succession” in action.
(For the original copy of the tablet, see R. Campbell Thompson, Assyrian Medical Texts (London: H. Milford / New York: Oxford University Press, 1923; reprinted, Osnabrück: Otto Zeller Verlag, 1983), 105,1 (=K.4023, col. iv, and thus probably from Nineveh).
I have cited the text according to Hermann Hunger, Babylonische und assyrische Kolophone, Alter Orient und Altes Testament 2 (Neukirchen-Vluyn: Neukirchener Verlag / Kevelaer: Verlag Butzon and Bercker, 1968), no. 533, with corrections from Yaakov Elman, “Authoritative Oral Tradition in Neo-Assyrian Scribal Circles,” Journal of the Ancient Near Eastern Society 7 (1975), 19-32, here 31.)
Salves (and) bandages: tested (and) checked, which are ready at hand, composed by the ancient sages from before the flood, which in Suruppak in the second year of Enlil-bani, king of Isin, Enlil-muballit, sage of Nippur, bequeathed.
Although the number of apkallū is unspecified in this text, the indication of plurality of sages and the antediluvian time frame strongly suggest an association with the seven sages known from traditions such as Bīt mēseri and the ULKS.
The fact that the tablet claims the apkallū composed these recipes bolsters the authority (by invoking these beings associated with Ea) and legitimacy (by asserting antiquity) of the recipes contained in the text.

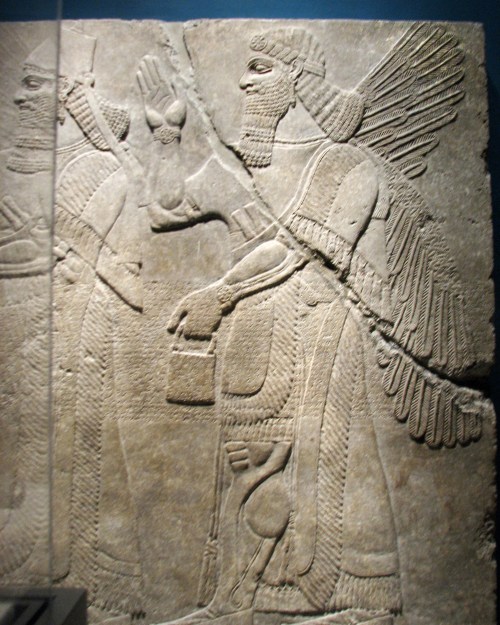
This depiction of a fish-apkallū of the parādu-fish type guarded the entrance to the temple of Ninurta at Nimrud.
A fish’s head can be seen on the apkallu’s head, and its skin hangs down over the back of his body.
It is important to recall that the so-called Seven Sages of Sumeria were apkallū of this type.
Neo-Assyrian era, 865-860 BCE.
From the Temple of Ninurta, Nimrud (ancient Kalhu; Biblical Calah), northern Mesopotamia, Iraq. (The British Museum, London).
Osama Shukir Muhammed Amin FRCP (Glasg)
http://www.ancient.eu/image/2708/
But I do not think that is its primary purpose. The claim is not made in the context of a ritual; so it does not primarily function to create ritual power.
Rather, the claim occurs in a colophon, a label that communicates something about the tablet for other would-be readers/users of it. The invocation of the apkallū and a claim to antediluvian knowledge in a colophon intends therefore to affect the social situation in which the tablet is used.
In this case the colophon credentials a human being as the possessor of antediluvian knowledge (i.e., medical recipes). Revealed by primeval apkallū, mediated to the human sage Enlil-muballit, and transmitted, presumably, by means of various copyists to the present possessor, AMT 105,1 implies the same notion of succession as the ULKS.
A similar idea is probably attested in KAR 177, obv. iv 25-32, a text containing hemerologies, which reads:
Favorable days. According to the seven s[ages(?)].
Duplicate of a tablet from Sippar, Nippur, Babylon, Larsa, Ur, Uruk, and Eridu.
The scholars excerpted, selected, and gave it to Nazimuruttash, king of the world.
(The tablet is from Assur and presumably the NA period. The text and restorations follow W. G. Lambert, “Ancestors, Authors, and Canonicity,” Journal of Cuneiform Studies 11 (1957), 1-14, here 8.
Lambert also gives the remainder of the colophon, rev. iv 1-3 (8), which is of no interest in this context, and sets out von Soden’s readings in a follow-up note (“Ancestors, Authors, and Canonicity [JCS XI, 1-14]: Additions and Corrections,” Journal of Cuneiform Studies 11 [1957], 112).
It seemed highly unlikely to the editor (Lambert) that the seven cities named in the text represented the seven exemplars from which the scribe worked. In other words, it seems unlikely that the scribe was looking at seven different copies while writing his own tablet.
Instead, Lambert proposed that the seven cities represent a succession of exemplars. Each of the exemplars was written by one of the seven sages one after another thereby creating a line of succession for the present tablet that extends back into earliest times.
The claim of this colophon, therefore, is that the tablet of hemerologies over which the ummânū labored goes back to the apkallū and ultimately originated in Eridu, the home city of Ea.
This again demonstrates an example of the “mythology of scribal succession” and an implicit assertion of antediluvian knowledge.”
Alan Lenzi, The Uruk List of Kings and Sages and Late Mesopotamian Scholarship, JANER 8.2, Brill, Leiden, 2008. pp. 149-51.