Selz: On the Astronomical Diaries of Babylon
“I cannot discuss here the philological evidence that anchors the biblical tradition in the historical charts. This is a different, albeit very important field which may support my arguments: I just mention one recent example: Jeremiah 39:3 may go back to an eye witness’s account of Nebuchadnezzar’s conquest of Jerusalem in 589 BCE.

Tablet VAT 4956 in the Berlin Museum details the positions of the moon and the planets during the year 37 of the reign of Nebuchadnezzar, king of Babylon, 567 BCE. This tablet is famous for confirming the destruction of Jerusalem in 586 BCE.
http://www.lavia.org/english/archivo/vat4956en.htm
This is indicated by my colleague Michael Jursa’s identification of the chief-eunuch Nabu-sharrussu-ukin, the biblical נכו שרםכים רכםרים or Nebu-Sarsekim, in an economic document from the sun-god temple in Sippar, dated to the “Month XI, day 18, year 10 Nebuchadnezzar, king of Babylon.”
(M. Jursa, “Nabû-šarrūssu-ukīn, rab ša-rēši, und ‘Nebusarsekim’ (Jeremiah 39:3),” NABU 5 (2008). Jursa’s translation of the document runs as follows:
“Regarding] 1.5 minas (0.75 kg) of gold, the property of Nabû-šarrūssu-ukīn, the chief eunuch, which he sent via Arad-Bānītu the eunuch to [the temple] Esangila: Arad-Bānītu has delivered [it] to Esangila.
In the presence of Bēl-usāti, son of Alpāya, the royal bodyguard, [and of] Nādin, son of Marduk-zēru-ibni. Month XI, day 18, year 10 [of] Nebuchadnezzar, king of Babylon.”
We may note here that the evaluation of this document provoked a broad discussion in scholarly literature and in the Internet.)
The Babylonian exile had a major impact on the development of Judaism, possibly even on the moulding of the apocalyptic traditions.
(Jeremiah 39:3 gives account of Nebuchadnezzar’s conquest of Jerusalem and his victory over the Judean King Zedekiah: The passage reports that all of the officers of the king of Babylon made their entry, and occupied the middle gate.)
(Kvanvig, Roots, writes: “The emergence of the apocalyptic traditions and literature presupposes both a direct contact with Mesopotamian culture in the Babylonian diaspora, and the syncretistic tendencies in Palestine in the post-exilic centuries.” See also Sarah Robinson, “The Origins of Jewish Apocalyptic Literature: Prophecy, Babylon, and 1 Enoch,” MS Thesis, University of South Florida, 2005.)
The background of this “knowledge transfer,” however, is the scholarly situation as just described. I say this not to deny the contribution of mere story-telling and fantastic lore to the growth of the corpus of apocalyptic literature, but we cannot neglect the scholarly and even empirical background of the underlying world-view.
Indeed, this may provide the best explanation for why so many different topics and stylistic features are fused in the extant Enochic traditions.

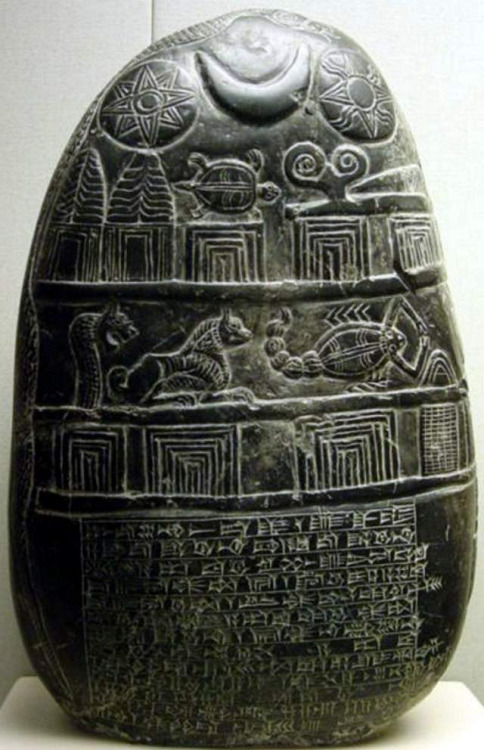
The Venus Tablet of Ammisaduqa, which is tablet 63 in the Enuma Anu Enlil sequence, preserves the astronomical observations of Venus during the 1st Millennium BCE.
This tablet is dated back to the mid-7th Century BCE, during the reign of King Ammisaduqa.
http://fineartamerica.com/featured/2-venus-tablet-of-ammisaduqa-7th-century-science-source.html
What concerns us here is the heuristic attitude of Mesopotamian scholarship. Even in the late Seleucid period this scholarship remains basically “holistic” or “monistic” in the way that it links all sorts of empiricism, as may be demonstrated with examples from the famous “Astronomical Diaries.”
(We follow here the unpublished manuscript of G. Graßhoff, “The Diffusion of Knowledge: From Babylonian Regularities to Science in the Antiquity” (paper presented at the 97th Dahlem Workshop on Globalization of Knowledge and its Consequences at the Dahlem Konferenzen, Berlin, 18-23 November 2007).
In the fifth year of Darius III (331 BCE) we find a series of astronomical observations:
“Day 13 [20 September]: Sunset to moonrise 8. There was a lunar eclipse. Its totality was covered at the moment when Jupiter set and Saturn rose. During totality the west wind blew, during clearing the east wind. During the eclipse, deaths and plague occurred.
Day 14: All day clouds were in the sky …”
The reports then continue with observations from the “Burse of Babylon”; commodity prizes are given together with the positions of the planets in the zodiacal signs.
“That month, the equivalent for 1 shekel of silver was: barley . . . at that time, Jupiter was in Scorpio; Venus was in Leo, at the end of the month in Virgo; Saturn was in Pisces; Mercury and Mars, which had set, were not visible.”
The reports further continue with the famous account of the downfall of the Persian empire in the same year, after the battle at Gaugamela, north of Mosul (331 BCE).”
(H. Hunger, ed., Astronomical Diaries and Related Texts from Babylonia, vol. 2: Diaries from 261 BCE to 165 BCE (Denkschriften der philosophisch-historischen Klasse 210; Wien: Verlag der Österreichischen Akademie der Wissenschaften, 1989), pp. 175-6.)
Gebhard J. Selz, “Of Heroes and Sages–Considerations of the Early Mesopotamian Background of Some Enochic Traditions,” in Armin Lange, et al, The Dead Sea Scrolls in Context, v. 2, Brill, 2011, pp. 786-7.




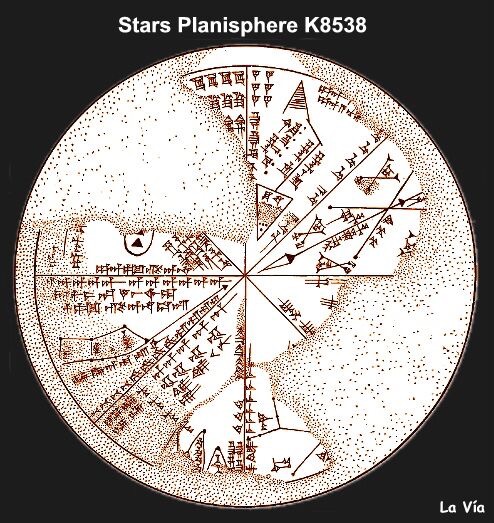





![Assyrian star planisphere found in the library of the Assyrian king Ashurbanipal (Aššur-bāni-apli – reigned 668-627 BCE) at Nineveh. The function of this unique 13-cm diameter clay tablet, in which the principal constellations are positioned in eight sectors, is disputed. The texts and drawings appear to be astro-magical in nature. Kuyunjik Collection, British Museum, K 8538 [= CT 33, 10]. London. http://www.staff.science.uu.nl/~gent0113/babylon/babybibl.htm](https://therealsamizdat.com/wp-content/uploads/2015/04/babylonian-star-chart.jpg?w=500)




![http://doormann.tripod.com/asssky.htm Assyrian star map from Nineveh (K 8538). Counterclockwise from bottom: Sirius (Arrow), Pegasus + Andromeda (Field + Plough), [Aries], the Pleiades, Gemini, Hydra + Corvus + Virgo, Libra. Drawing by L.W.King with corrections by J.Koch. Neue Untersuchungen zur Topographie des Babilonischen Fixsternhimmels (Wiesbaden 1989), p. 56ff.](https://therealsamizdat.com/wp-content/uploads/2015/05/assyrian-star-map-from-nineveh.jpg?w=500)




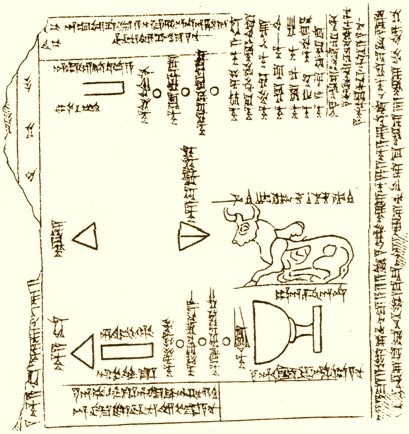
![Illustration: Tablet sculptured with a scene representing the worship of the Sun-god in the Temple of Sippar. The Sun-god is seated on a throne within a pavilion holding in one hand a disk and bar which may symbolize eternity. Above his head are the three symbols of the Moon, the Sun, and the planet Venus. On a stand in front of the pavilion rests the disk of the Sun, which is held in position by ropes grasped in the hands of two divine beings who are supported by the roof of the pavilion. The pavilion of the Sun-god stands on the Celestial Ocean, and the four small disks indicate either the four cardinal points or the tops of the pillars of the heavens. The three figures in front of the disk represent the high priest of Shamash, the king (Nabu-aplu-iddina, about 870 B.C.) and an attendant goddess. [No. 91,000.]](https://therealsamizdat.com/wp-content/uploads/2015/01/an00582752_001_l.jpg?w=500)


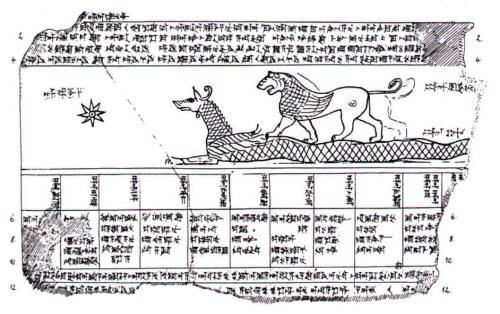
![Illustration: Tablet inscribed with a list of the Signs of the Zodiac. [No. 77,821.]](https://therealsamizdat.com/wp-content/uploads/2015/01/015.png?w=500)
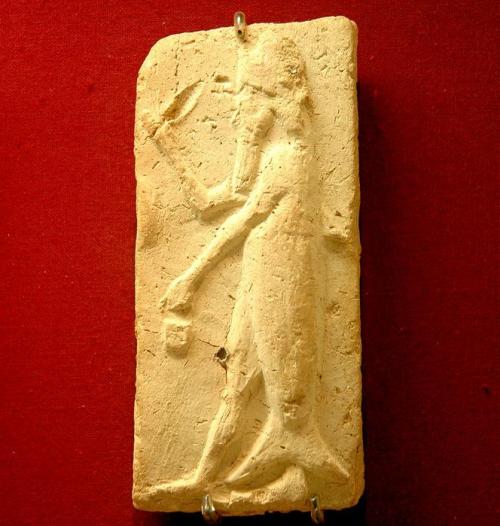
![Illustration: Shamash the Sun-god rising on the horizon, flames of fire ascending from his shoulder. The two portals of the dawn, each surmounted by a lion, are being drawn open by attendant gods. From a Babylonian seal cylinder in the British Museum. [No. 89,110.]](https://therealsamizdat.com/wp-content/uploads/2015/01/an00323246_001_l.jpg?w=500)