Curnow: Atrahasis is More Historical than Noah
“Atrahasis is an interesting figure. By surviving the flood he and his wife became the living links between the antediluvian and postdiluvian ages. They also seem to have been the only human beings to have been made immortal (Leick 2001, p. 83).
More than once the narrative presents Atrahasis talking to Ea, the god of wisdom, and this is perhaps the basis for his own reputation for wisdom. On one occasion he is clearly asking the god to explain a dream to him. However it is also said that his father was called Shuruppak, who was the last king of the city-state of Shuruppak before the great flood.
(Excavations at Shuruppak have uncovered evidence of very substantial flooding there in around 2750 BCE).

MS in Sumerian on clay, Sumer, ca. 2600 BC.
Context: For the Old Babylonian recension of the text, see MSS 2817 (lines 1-22), 3352 (lines 1-38), 2788 (lines 1-45), 2291 (lines 88-94), 2040 (lines 207-216), 3400 (lines 342-345), MS 3176/1, text 3, and 3366.
Commentary: This Early Dynastic tablet represents the earliest literature in the world. Only three texts are known from the dawn of literature: The Shuruppak instructions, The Kesh temple hymn, and various incantations (see MS 4549).
The instructions are addressed by the antediluvian ruler Shuruppak to his son Ziusudra, who was the Sumerian Noah, cf. MS 3026, the Sumerian Flood Story, and MS 2950, Atra-Hasis, the Old Babylonian Flood Story.
The Shuruppak instructions can be considered the Sumerian antecedents of the Biblical Ten Commandments and proverbs of the Bible:
Line 50: Do not curse with powerful means (3rd Commandment); lines 28: Do not kill (6th Commandment); line 33-34: Do not laugh with or sit alone in a chamber with a girl that is married (7th Commandment); lines 28-31: Do not steal or commit robbery (8th Commandment); and line 36: Do not spit out lies (9th Commandment).
http://www.uned.es/geo-1-historia-antigua-universal/new%20website/IRAK/CIUDADES/instrucciones_de_shurupak.htm
The names of both Shuruppak (the king) and Atrahasis (as Ziusudra) appear in a Sumerian work known as The Instructions of Shuruppak to His Son Ziusudra. The earliest surviving fragments of this have been dated to around 2500 BCE. The work includes a variety of proverbs, aphorisms and observations within a framework indicating that this is Shuruppak’s advice to his son.
Just before the final flourish in which Shuruppak pays his valedictory respects to Nisaba comes line 278, which could either be regarded as a final aphorism, or as a summation of the entire text: “The gift of wisdom [is like] the stars (of heaven).” (Alster 1974, p. 51).
Atrahasis is therefore the beneficiary of both the divine wisdom of Ea and the human wisdom of Shuruppak, and most fittingly called “extra-wise.”
Israel
While there are few believers in Thoth or Marduk in the world today, the idea that anything that appears in the Bible should be treated as mythology will doubtless seem objectionable to some, but there is no obvious reason why Atrahasis should be treated as mythological while Noah is treated as historical.
Indeed Dalley (2000, p. 2) sees in “Noah” a possible derivation from “Utnapishtim,” the Akkadian name of the survivor of the Mesopotamian flood. For present purposes the most important antediluvian figure in the Bible is without doubt Enoch, although in fact the Bible says very little about him and what it does say is vague and confused.
Genesis (4, 5) seems to draw on two different and conflicting genealogies, one of which makes Enoch the son of Cain, the other makes him the son of Jared, a seventh-generation descendant of Adam through the line of Seth.

Book of Enoch.
http://theremnanttrust.info/book-of-enoch/
In an enigmatic phrase it is said that “God took him” (Genesis 5:24), and this came to be understood to mean that he ascended into heaven. Towards the end of the first millennium BCE a literature began to grow around Enoch and there survive three books concerning him, sometimes known as the Ethiopic (1), Slavonic (2) and Hebrew (3) Enochs after the languages in which they have been preserved.
Debates concerning the dating of these texts have been as long as they have been inconclusive, and some have argued for 2 Enoch and 3 Enoch to be from the late first millennium AD, and so outside the scope of this work.
Fortunately, it is 1 Enoch that is of most interest here, and for that an earlier date is agreed.”
Trevor Curnow, Wisdom in the Ancient World, Bloomsbury, 2010, pp. 41-2.

![Assyrian star planisphere found in the library of the Assyrian king Ashurbanipal (Aššur-bāni-apli – reigned 668-627 BCE) at Nineveh. The function of this unique 13-cm diameter clay tablet, in which the principal constellations are positioned in eight sectors, is disputed. The texts and drawings appear to be astro-magical in nature. Kuyunjik Collection, British Museum, K 8538 [= CT 33, 10]. London. http://www.staff.science.uu.nl/~gent0113/babylon/babybibl.htm](https://therealsamizdat.com/wp-content/uploads/2015/04/babylonian-star-chart.jpg?w=500)
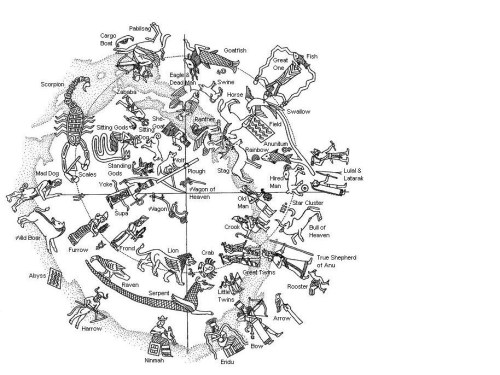
September 20, 2015
Melvin: Who Built the First City? Cain? Enoch? Chousor? Or Nimrod?
“The portrayal of the rise of civilization in Genesis 1–11, on the other hand, is generally negative and is devoid of any hint of divine assistance or bestowal of the arts of civilization. A key text in this regard is Genesis 4:20–22, in which the descendants of Cain found the guilds of nomadic shepherding, music, and metallurgy.
The statements are brief, merely indicating that Jabal was the founder of nomadic shepherding, Jubal was the founder of the art of music, and Tubal-cain was the first to work with metals.
If one considers the entirety of Genesis 4, one may also add to the list of new developments animal husbandry (v. 2), agriculture (v 2), city-building and urbanism (v 17), and polygamy (v 19).
An aerial view of the Ziggurat of Ur.
Gunkel, following Wellhausen, reads the account as brief fragments of what were originally much fuller mythological narratives and suggests that they may originally have referred to deities, but even if this reading is correct for the original myths, the text in its present form has been largely de-mythologized, and the individuals and their accomplishments are completely human.
(Hermann Gunkel, Genesis (trans. Mark E. Biddle; Macon: Mercer University Press, 1997), p. 50. Wellhausen argues that the genealogies in Genesis 4 and Genesis 5 refer to the same individuals and were originally identical.
See Julius Wellhausen, Prolegomena to the History of Israel (New York: Meridian, 1957), pp. 308–09; see also E. A. Speiser, Genesis (AB 1; Garden City: Doubleday, 1964), pp. 35–36. If this is the case, then it is important to note that Cain’s genealogy has been distinguished from Seth’s by the insertion of episodes which give the entire list a negative overtone (e.g., Cain’s fratricide, Lamech’s murders).
See John Skinner, A Critical and Exegetical Commentary on Genesis (2d ed.; ICC; Edinburgh: T&T Clark, 1930), p. 115. Since the statements concerning the arts of civilization appear only in the Cainite genealogy, it is likely that their inclusion is for the sake of bringing upon them “guilt by association” with the dark line of Cain.
Ruins and Plan of the Anu Ziggurat and the White Temple. Uruk ( Present-day Warka, Iraq). c. 3300-3000 BCE.
https://www.pinterest.com/pin/168814686005734256/
Seth’s genealogy, by contrast, includes a number of statements which give a more positive impression to the whole list (e.g., humans calling on the name of Yahweh, Enoch walking with God). However, Gordan J. Wenham makes a case against seeing the two genealogies as originally identical. See Gordon J. Wenham, Genesis 1–15 (WBC, 1; Waco: Word, 1987), p. 110.)
Further indication of the human origin of civilization in Genesis 1–11 appears in the motif of city-building and urbanism. Interestingly, Mesopotamian myths attribute the origin of the earliest cities to the work of gods (e.g., Marduk’s construction of Babylon) or semi-divine heroes (e.g., Gilgamesh’s building of the walls of Uruk), while Genesis 4:17 attributes the first city to Cain, who names it after his first son, Enoch, with no indication of divine assistance.
(Westermann notes that the reading of the Hebrew text seems to indicate that it was actually Enoch who built the city, rather than Cain, until one reaches the phrase כשם כנן “according to the name of his son,” which he suggests may originally have read simply כשמו “according to his name” (Genesis 1–11, 327).
He further argues that it would be unusual for Cain to have been both the founder of agriculture and the first city-builder. Such accounts of the development of civilization typically do so by a succession of births in which each generation makes but one new contribution.
But this is not always the case, as The Phoenician History shows by attributing to Chousor (Kothar) the arts of magic, divination, prophecy, sailing, and fishing (see Albert I. Baumgarten, The Phoenician History of Philo of Byblos: A Commentary [Leiden: Brill, 1981], p. 143).)
Similarly, the building of several key cities in Mesopotamia, as well as the formation of the world’s first empire, is attributed to Nimrod in Genesis 10:8–12.”
David P. Melvin, “Divine Mediation and the Rise of Civilization in Mesopotamian Literature and in Genesis 1-11,” Journal of Hebrew Scriptures, 2010, pp. 7-9.
Share this: