Temple of Bel, Temple of Marduk, Temple of Babylon, E-Sagila
“He says of it:
“Ka-khilibu, the gate of glory, as well as the gate of E-Zida within E-Sagila, I made as brilliant as the sun. The holy seats, the place of the gods who determine destiny, which is the place of the assembly (of the gods), the holy of holies of the gods of destiny, wherein on the great festival (Zagmuku) at the beginning of the year, on the eighth and the eleventh days (of the month), the divine king (Merodach), the god of heaven and earth, the lord of heaven, descends, while the gods in heaven and earth, listening to him with reverential awe and standing humbly before him, determine therein a destiny of long-ending days, even the destiny of my life; this holy of holies, this sanctuary of the kingdom, this sanctuary of the lordship of the first-born of the gods, the prince, Merodach, which a former king had adorned with silver, I overlaid with glittering gold and rich ornament.”
Just within the gate was the “seat” or shrine of the goddess Zarpanit, the wife of Merodach, perhaps to be identified with that Succoth-benoth whose image, we are told in the Old Testament, was made by the men of Babylon.
E-Zida, “the firmly-established temple,” was the chapel dedicated to Nebo, and derived its name from the great temple built in honour of that deity at Borsippa. As Nebo was the son of Merodach, it was only fitting that his shrine should stand within the precincts of his father’s temple, by the side of the shrine sacred to his mother Zarpanit.
It was within the shrine of Nebo, the god of prophecy, that the parakku, or holy of holies, was situated, where Merodach descended at the time of the great festival at the beginning of the year, and the divine oracles were announced to the attendant priests.
The special papakha or sanctuary of Merodach himself was separate from that of his son. It went by the name of E-Kua, “the house of the oracle,” and probably contained the golden statue of Bel mentioned by Herodotus.
Nebuchadnezzar tells us that he enriched its walls with ”glittering gold.” Beyond it rose the stately ziggurat, or tower of eight stages, called E-Temen-gurum, “the house of the foundation-stone of heaven and earth.” As was the case with the other towers of Babylonia and Assyria, its topmost chamber was used as an observatory.
This illustration depicts the dual ziggurats of E-temen-anki and the Temple of Bel, conflating them as E-Sagila, the Temple of Marduk.
http://www.dalamatiacity.com/urantia-clues23.htm
No temple was complete without such a tower; it was to the Babylonian what the high-places were to the inhabitants of a mountainous country like Canaan. It takes us back to an age when the gods were believed to dwell in the visible sky, and when therefore man did his best to rear his altars as near to them as possible. “Let us build us a city and a tower,” said the settlers in Babel, “whose top may reach unto heaven.”
The Babylonian Bel, accordingly, was Merodach, who watched over the fortunes of Babylon and the great temple there which had been erected in his honour. He was not the national god of Babylonia, except in so far as the city of Babylon claimed to represent the whole of Babylonia; he was simply the god of the single city of Babylon and its inhabitants.

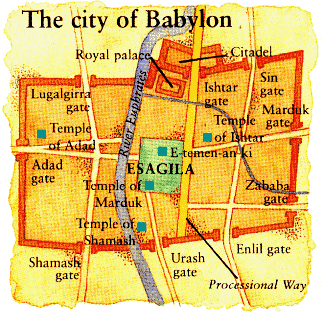
This map depicts more clearly the relative positions of Etemenanki and the Temple of Marduk.
Map of Babylon
Creator
Jona Lendering
Licence
Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International
Linked
Babylon, Babylonian Empire, Capture of Babylon (Herodotus), Esagila, Etemenanki (the “Tower of Babel”), Zopyrus
Categories
Babylonia
http://www.livius.org/pictures/a/maps/map-of-babylon/
http://www.livius.org/place/etemenanki/
He was but one Baal out of many Baalim, supreme only when his worshippers were themselves supreme. It was only when a Nebuchadnezzar or a Khammuragas was undisputed master of Babylonia that the god they adored became “the prince of the gods.”
But the other gods maintained their separate positions by his side, and in their own cities would have jealously resented any interference with their ancient supremacy. As we have seen, Nabonidos brought upon himself the anger of heaven because he carried away the gods of Marad and Kis and other towns to swell the train of Merodach in his temple at Babylon.”
A.H. Sayce, Lectures on the Origin and Growth of Religion as Illustrated by the Religion of the Ancient Babylonians, 5th ed., London, 1898, pp. 94-7.
