An Excerpt from The Fall of the Angels
“How did the story about the fall of the angels relate to biblical tradition? Why is it only hinted at there, and not incorporated into the canon in more complete form? Two general points may be offered in response to these questions.
First, the story presupposes, rather than lies behind, the Hebrew Bible and, thus, is to be regarded as a development, indeed interpretation, of what later came to be recognized as canonical. Second, the communities which produced the story did so by transforming the biblical tradition through the dual filters of apocalyptic dualism and their own social contexts.
These points have to be taken into account when considering how it was that “the day of the Lord” of the exilic and post-exilic prophets could be absorbed into the notion of a final apocalyptic battle in later early Jewish literature. Was this shift from prophetic to apocalyptic eschatology the result of an attempt to reject the foreign domination by Hellenistic rulers—such as the Ptolemies in Egypt and the Seleucids in Syria—in the wake of Alexander the Great’s conquests?
Or was this growing dualism a reflection of the breach between urban and rural culture? Or, by contrast, did the apocalyptic religious tradition re-present knowledge gleaned from the “foreign” sciences of its day as divine revelation, doing so long before the Greeks came on the scene?
There were yet other stories in the Ancient Near East that had been told long time and retold in the Greek world. Those stories were adapted to the current social situation and to the clash of civilizations. (sic).
The famous passage from Genesis 6:1-4 played a central role in the development of apocalyptic traditions. The biblical tradition itself is ambiguous; it conveys a story about ancient “heroes”, on the one hand, and the “sons of the gods”, on the other. What these figures have to do with the destruction brought about through the Great Flood in the following narrative (Genesis 6:5ff.) constitutes the first question to be examined in this volume.
The contribution by Ronald Hendel does so by exploring possible parallels to the biblical story in the Ancient Near East. One of the most significant traditions to throw light on the biblical account is shown to be the Atrahasis Epic. If read alongside this epic, the ruptures and ambiguities within the Genesis narrative, which involves the insertion of a polytheistic conflict between deities into a monotheistic narrative about God and creation, do not appear so conspicuous or unexpected.
This is further illustrated by the common motif that has the lower world flooded by the heavenly world in order to prevent the superhuman inhabitants of the lower world from becoming too powerful. The attempt by the gods above to destroy the younger and smaller ones reaches a truce in the form of a treaty or alliance. This is how Genesis chapters 6-9 may be comprehended as a complete narrative and, in addition, came to include the passage in 6:1-4.
A tradition about a revolt in a heavenly palace is preserved in the Babylonian Atrahasis Epic, also known through the Baal-Cycle from Ugarit and the Hethitic Kumarbi Epic, has also influenced Greek mythology which tells of the conflict between Zeus, on the one hand, and his tyrannical murderer-father and the Titans his helpers, on the other. In this volume, Jan Bremmer argues impressively that the “Titans” of the story are actually not destroyed. The fear of their possible return persists and remains an irrepressible potential and threat.
How astronomic observation, the interpretation of stars as deities living in a distant world, and scientific knowledge are coalesced into the traditional image of God is shown by Matthias Albani in his analysis of Isaiah 14.

The Fall of the Rebel Angels is an oil-on-panel by Flemish renaissance artist Pieter Bruegel the Elder, painted in 1562. It is currently held and exhibited at the Royal Museums of Fine Arts of Belgium in Brussels.
Bruegel’s depiction of this subject is taken from a passage from the Book of Revelation (12, 2-9) and reveals the artist’s profound debt to Hieronymous Bosch, especially in the grotesque figures of the fallen angels, shown as half-human, half-animal monsters.
Together with Dulle Griet and The Triumph of Death, which have similar dimensions, it was probably painted for the same collector and destined to become part of a series.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/The_Fall_of_the_Rebel_Angels_(Bruegel)
For Albani, the myth of the morning star that rises at night only to be driven away and dissolved by the light of the sun is discernible in a story about the power of God who, though rivaled by the smaller stars, is never surpassed by them.
The fact that the Isaiah account may be dated to the exilic period—and so is similar to expulsion of the throne pretender mentioned in Ezekiel 28—strengthens the likelihood that it functioned as a story of consolation. The image of the rise and fall of Helel was later translated into “Lucifer” in Latin tradition. The interpretation is depicted in Figure No. 2.
No direct line can be drawn from the Isaiah narrative to the Enochic apocalyptic literature and its Gnostic adaptation. The apocalyptic and cosmological dualisms of the latter fundamentally changed the religious tradition into something cosmic, super-historical, and superhuman.”
Christoph Auffarth & Loren T. Stuckenbruck, eds., “The Centre for Power for Evil: Its Origins and Development,” in The Fall of the Angels, Brill, 2004.

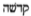 nor the qadištu nor the nu-gig are to be reckoned as sacred prostitutes, it remains necessary to prove that there was no such institution as sacred prostitution in Mesopotamia in spite of its widespread reputation among scholars, to which I would like to return in the conclusion.
nor the qadištu nor the nu-gig are to be reckoned as sacred prostitutes, it remains necessary to prove that there was no such institution as sacred prostitution in Mesopotamia in spite of its widespread reputation among scholars, to which I would like to return in the conclusion.