Erica Reiner on the Etiological Myth of the “Seven Sages”
“The bilingual text LKA No. 76 has been characterized by Ebeling, in the catalog LKA p. x, as “Zweisprachiger Text von den ‘sieben Söhnen von Nippur’, mystischen Inhalts.” The obverse of the text contains an unusual self-description given by the “sons of Nippur,” to which I have been unable to find a parallel, but the much smaller portion preserved of the reverse, which most likely is an altogether different composition, is a duplicate to two texts from Kouyunjik edited by O.R. Gurney, JRAS 1935 459 ff., which deal with the apkallu’s who, under the designation “Seven Sages” have received repeated attention in Assyriological literature.
The reverse of LKA 76, which shall be my sole concern in this paper, as well as an unpublished fragment from Kouyunjik copied by Geers, permits us to establish the historical and mythological significance of these personages. [ … ]
Translation
- 1′-2′. [Adapa,] the purification priest of Eridu
- 3′-4′. [ … ] who ascended to heaven.
- 5′-6′. They are the seven brilliant apkallu’s, purādu-fish of the sea,
- 7′-9′. [sev]en apkallu’s “grown” in the river, who insure the correct functioning of the plans of heaven and earth.
- 10′-13′. Nunpiriggaldim, the apkallu of Enmerkar, who brought down Ištar from heaven into Eanna;
- 14′-17′. Piriggalnungal, stemming from Kiš, who angered Adad in heaven so that he let no rain and (hence) vegetation be in the country for three years;
- 18′-23′. Piriggalabzu, stemming from [Eridu] who . . . . and thus angered Ea in the Apsû so that he . . . [cut (?) the cords from (?) the seal around his neck (?)] . . .
- 24′-27′. The fourth (is) Lu-Nanna, (only) two-thirds apkallu, who drove the ušumgallu-dragon from Eninkarnunna (var. Eninkiagnunna), the temple of Ištar of Šulgi.
- 28′-31′. [ . . . ] of human descent, whom (pl.) the lord Ea had endowed with a broad understanding.
. . . If the restorations [MIN] in lines 3’ff are correct, this section enumerates or addresses apkallu’s . . . (See footnote 3, below).
(Footnote 3: While the main concern of these pages is to follow the apkallu’s into their mythological past, it should be mentioned that their role in the here edited text, as well as in other rituals to be mentioned presently, is an apotropaic one (having the power to avert evil influences or bad luck); indeed, copies … of the text under discussion may well represent a tablet of the series bīt mēsiri, for which see G. Meier, AfO 14 139 ff.

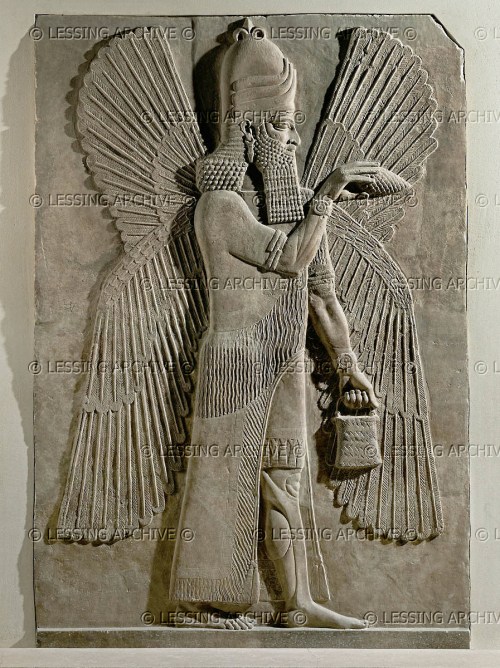
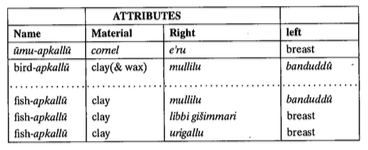
Bird Apkallū and Fish Apkallū, side by side. Apkallū statuettes of this design were buried in appropriate places in the home of a Babylonian exorcist. They were believed to have prophylactic qualities, guarding the home from evil.
This is made likely by the content as well as the style of the invocations alternating with ritual directions, and the latter have been here restored on the basis of this similarity. Moreover, A rev. 5′ f. recalls the catchline of 4R 21 B, a recension of Tablet II of bīt mēsiri … the number, shape, and use of these apotropaic figures varies from text to text, apkallu being a general term for the fish-, bird-, or “Gilgameš“-like men (see Landsberger Sam’al 95 n. 227); thus, before the apkallu’s enumerated in lines 10′-27′, who are then summed up as being of human descent (ilitti amēlūti), the text mentions the seven apkallu’s who are purādu-fish and seven apkallu’s who were “created” (Sumerian “grown”) in the river.)
As A rev. 16’ff. shows, the rites were performed for the benefit of a patient (LÚ.GIG); they include, according to A rev. 10’f., fashioning of apotropaic apkallu-figurines, or, according to lines 3’ff. (in copy C), figurines of suhurmāšu-fish.”
Erica Reiner, “The Etiological Myth of the “Seven Sages,” Orientalia, v. 30, No. 1, 1961, pp. 1-6.