Nakamura–Rimbaud’s Derangement of All the Senses, Magic, and Archeology
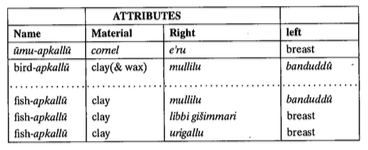
“Curiously, archaeological research has not fully exploited the evocative cooperation between text, iconography, material, and deposition in this apotropaic practice. Rather, it has been the art historical and Assyriological traditions that have provided the most thorough deliberations on the ritual.
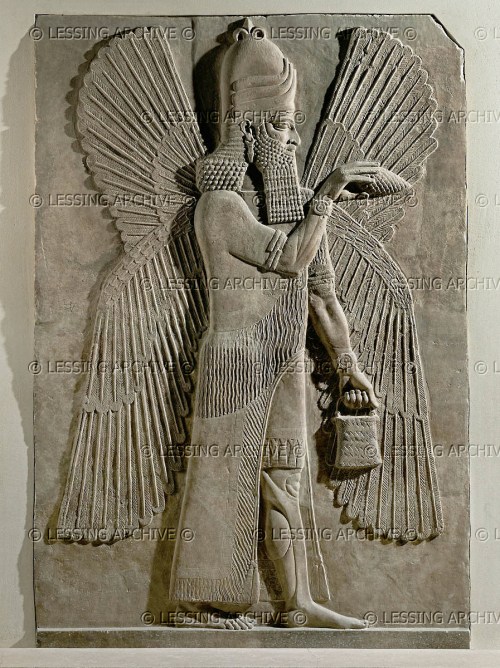
Iconographic analyses present detailed visual descriptions of the figurines (Klengel-Brandt 1968; Rittig 1977; Van Buren 1931), and trace out a visual typology of apotropaic images (Green 1993; Wiggermann 1993), while textual analysis investigates the symbolic logic of apotropaic prescription and the mythological identities of the figures (Wiggermann 1992).
Two long-awaited volumes no doubt will provide further analyses of particular site assemblages (Green forthcoming) and the apotropaic figurines in general (Ellis forthcoming). Despite the richness of textual and archaeological data, an anthropological perspective is distinctly lacking; however, such research would considerably enrich our views of this remarkable ancient practice.
Regrettably, studies of previously excavated materials have not exploited the diverse range of approaches afforded by modern social sciences. While previously excavated sites and materials admittedly do not often lend themselves to the analytical and interpretive techniques most favored by archaeologists, such data should not be omitted from modern reconsideration and inquiry simply because they present a special challenge for substantive interpretation (see Meskell 1999).
There is, in fact, adequate data to perform detailed contextual and spatial analyses of the apotropaic practice at certain Neo-Assyrian sites. Furthermore, I would argue that conventional interpretations in archaeology — still oriented toward explanation and meaning — fail to get at the most compelling aspects of ancient magic, exactly that which makes it magical.
Magic surely presents something beyond the reach of representational or functional interpretations and thus demands a different perspective. What is required is an evocation of magic that aims directly at the caesura between meaning and matter and delves into the shadowy processes of materializing experience, belief, and value.
Perhaps it is not surprising that archaeology, with only material traces of human activity to work with, has left the critical study of magic to other disciplines. It is revealing that “magic” is generally invoked as an explanation for those slippery things, processes, and occurrences that our rational and linguistic varieties of logic can’t quite master.
From this vantage, magic has become something more suitable for explaining than for being explained. But as Mauss (1972) decisively observed in A General Theory of Magic, magic is as much a way of doing as a way of thinking.
We should consider, then, not a logic but an aesthetics of magical practice, as a particular way of making sense (Gosden 2001). And this way of doing engages a radical materiality that not only enacts the mutual constitution of subjects and objects, but provides the condition for such discursive practices.
A consideration of materiality vis-à-vis magic, then, does not presume and continue the anthropological pursuit of finding meaning in matter, the well-rehearsed terrain of discovering how various cultures construct and inscribe meaning in their artifacts.
What is magical or forceful in certain artifacts evades such fixed and flattened analyses since processes of abstraction do not account for the “untranscended materiality” or “plastic power” of the object that derives from the thing’s materialness itself (Pels 1998:101).
Impoverished attempts to discover the meaning or social context of a magical artifact, as it were, fall short not only because of an opacity of things, but also because our habituated ways of apprehending and constructing meaning threaten a veritable non-recognition of the things themselves.
This purifying analytical gaze effectively eviscerates matter of its very materiality — its innate capacity to continuously engage and enter into new relations. But recovering a recognition of things simply requires embracing the thingness of matter, namely, that insistent sensuousness of things that compels a confrontation with humans.
This move does not return us to problematic theories of materialism, but rather engages a notion of materiality as a dialectic and supplemental aesthetic of relating to.
Humans mime the animate in the inanimate, and the ideal in the real, to create and transform the world around them, only to be created and transformed right back. Such is the reality of matter: it “strikes back” (Pels 1998:91).
Within this framework I suggest that apotropaic figurine magic encompasses a process that enacts both a distinct mode of perception and a material event that renders a protected reality.
This discussion converges specifically on two aspects of magic: first, how magic capitalizes on a tension between the social construction of meaning and the radical autonomy of matter, and second, how magical perception, in the way of poetic action, masters the unknown by recovering and performing a “derangement of all the senses.” (Rimbaud 1967:302 and Deleuze 1993).
From such a viewpoint, Mesopotamian magic neither constitutes nor opposes a “rational” mode of knowing the world, but rather moves alongside in tandem, as counterpoint in a polyphonic system of knowledge. From this perspective, magic engages a sensuous metaphysics and grounds the possibility of a distinct socio-religious worldview.”
Carolyn Nakamura, “Mastering matters: magical sense and apotropaic figurine worlds of Neo-Assyria,” Archaeologies of materiality (2005): 19-22.