Kvanvig: Divine Origin of Antediluvian Texts
“Enuma Elish was written to promote Marduk as the head of the pantheon, reflecting the position of Babylon at the end of the second millennium. This was a new invention in Mesopotamian theology. To promote this new theology the author added a postscript in which he claims a divine origin for his work:
“This is the revelation which an Ancient, to whom it was told,
wrote down and established for posterity to hear.”
(Enuma Elish VII, 157-8. Translation according to van der Toorn, Scribal Culture, p. 212.)
The word translated “revelation,” taklimtu, literally means “demonstration.” The term preserves a memory of the time when revelation was thought of as a visual experience. In this case, however, the gods told the text to an Ancient, meaning that they had dictated it.

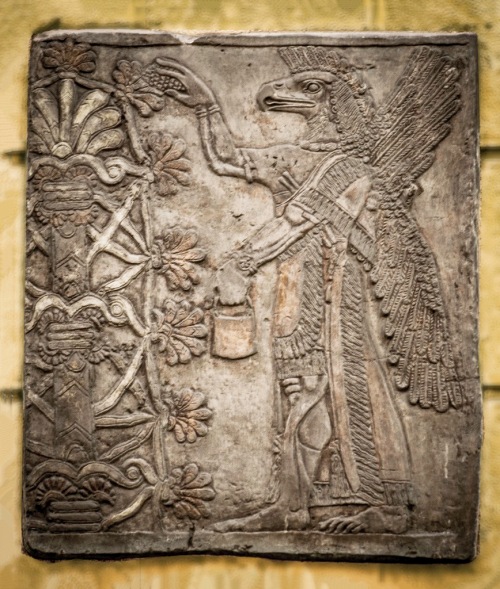
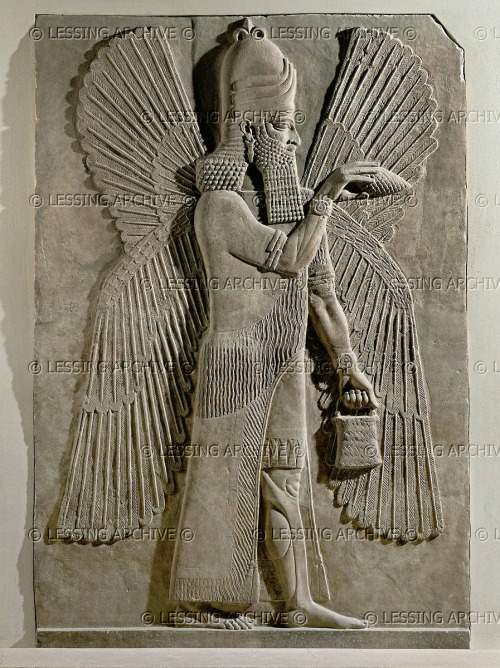
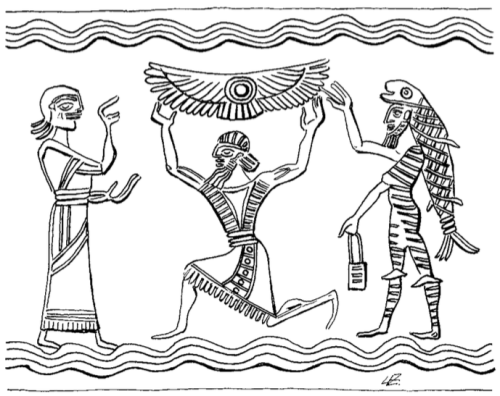
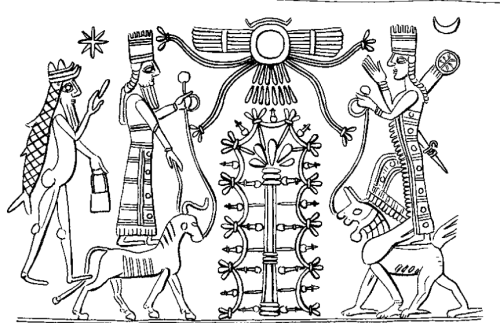
This is one of the few representations of a Mesopotamian pantheon that I have seen, allegedly adapted from a rock relief at Malatia (Anti-Taurus range).
From Professor Morris Jastrow’s Aspects of Religious Belief and Practice in Babylonia and Assyria, G.P. Putnam’s & Sons, 1911.
https://archive.org/details/aspectsofreligio00jast
http://wisdomlib.org/mesopotamian/book/myths-and-legends-of-babylonia-and-assyria/d/doc7167.html
Another version of this pantheon observes that Aššur is at the head of the procession, standing on two animals, including a snake-dragon or muššuššu. The rod and ring of sovereignty are in his right hand. I am not sure what he holds in his left hand.
Ištar (of Nineveh) is depicted seated on a throne, carried as usual by a lion, her sacred animal. She carries what Black and Green term a “chaplet,” a ring of temporal authority. The objects on the rear of her throne evoke her common depiction with maces and weaponry, appropriate for a goddess of love and war. Her throne is supported by indistinct figures of the Mesopotamian pandemonium. Winged scorpion-men, perhaps.
The third figure from right to left is said to be Sin, the Moon-god, mounted upon a winged bull. Like Aššur, he holds an object which could be the horn from a bull in his left hand, and the rod and ring of temporal sovereignty in his right.
The fourth figure from the right is believed to be Enlil or Marduk, like Aššur standing on a Muššuššu dragon. While this figure’s left hand is empty, raised in the gesture of greeting, he holds the rod and ring in his right hand.
The next figure is said to be Shamash, (or Šamaš), the sun god, mounted on a horse. He holds the rod and ring in his right hand, and greets with his left hand.
Adad is second from the left, with lighting bolts in his hands. Adad stands on a pair of winged bulls.
The final figure is believed to be a depiction of Ištar on a lion, either Ištar of Arbela or Ištar of Babylon.
See Place, Ninive et VAssyrie, Pl. 45, from which it would appear that the design was repeated three times on the monument.
See also Luschan, Ausgrabungen in Sendschirli , p. 23 seq.
For another procession of gods (on an alabaster slab found at Nimroud) see Layard, Monuments of Nineveh, i., Pl. 65.
http://www.wisdomlib.org/mesopotamian/book/aspects-of-religious-belief-and-practice-in-babylonia-and-assyria/d/doc7258.html
Finally, Jeremy Black and Anthony Green observe, “The best preserved of four similar panels of rock reliefs at Maltai, carved on the cliff face on the southern side of the Dehok valley, by the road leading from Assyria to the Upper Zab valley. (This reads as though Black & Green had actually visited the site).
Black and Green note that an Assyrian king, “probably Sennacherib (704-681 BCE),” flanks the seven depicted deities.
The version in Black and Green is reversed, with the procession facing to the left. From left to right, Black and Green identify Aššur on Muššuššu, followed by “his consort Mullisu enthroned on a lion,” Enlil or Sin on a lion-dragon, Nabu on a snake-dragon, Šamaš on a horse, Adad with lightening bolts, and Ištar on a lion.
Jeremy Black and Anthony Green, Gods, Demons and Symbols of Ancient Mesopotamia, 1992, p. 40.
https://books.google.co.th/books?id=pr8-i1iFnIQC&redir_esc=y
Anthony Green updated these comments in 1994 in Michwesen. B. “The best preserved of four similar panels of rock reliefs at Maltai, carved on the cliff face on the southern side of the Dehok valley, by the road from Assyria to the upper Zab valley. The Assyrian king, probably Sennacherib, flanks a procession of seven deities upon their animals. After F. Thureau-Dangin, Les Sculptures Rupestres de Maltai, RA 21 (1924), p. 187. For the beasts, cf. U. Seidl, RIA III s.v. “Gottersymbole und -attribute.”
Anthony Green, Mischwesen. B, 1994, p. 263.
https://www.academia.edu/2378476/Mischwesen_B._A.Green_
The Ancient put it down into writing and established it for future generations. This is very similar to what Kabti-ilāni-Marduk says about the revelation of the Poem of Erra, as van der Toorn also notes.
We can observe a similar feature in Gilgamesh. In the Old Babylonian version of the epic, wisdom is human knowledge acquired through life experience. In the Standard Babylonian version from the end of the second millennium this wisdom has become divine.
The editor added a prologue in which he pictures Gilgamesh as a man who has obtained hidden wisdom, inaccessible to others:
“he [learnt] the totality of wisdom about everything.
He saw the secret and uncovered the hidden,
he brought back a message from the antediluvian age.”
(Gilgamesh I, 6-8. Translation according to George, The Babylonian Gilgamesh Epic I, 539.)
The same theme reoccurs at the end of the composition, in tablet XI, where Gilgamesh meets Uta-napišti, the hero of the flood, who has become like the gods. Uta-napišti reveals secrets to Gilgamesh, referred to as “a hidden matter” and “a secret of the gods” (XI, 9-10, repeated in 281-2).
Van der Toorn sees the classification of writings as “revelations” and “secrets” in relation to the development from an oral to a scribal culture. Oral and written transmission existed together in the long time span of Mesopotamian culture, but at a certain time there came a change, i.e. at the end of the second millennium.
The written tradition became more important in the formation of new generations of scholars.
“From that moment on, students began to acquire their knowledge by copying texts rather than listening to a teacher; the master copy took the place of the master.”
(Van der Toorn, Scribal Culture, 218.)
The authority was transposed from the master to the text, and the text needed an authority that also included the master. Thus the construct was made about a written revelation from Ea to the apkallus and further in an unbroken chain down to the actual scholars.
They were the legitimate heirs of this written tradition; it was once revealed and therefore a secret belonging to their guild.
“To legitimize the written tradition, the Mesopotamian scholars qualified it as divine revelation; to preserve their privileged position as brokers of revealed knowledge, they declared it to be secret knowledge.”
(Ibid., 220.)
Even though we know that cause-effect constructions in the reconstruction of history cannot be one-dimensional, we find van der Toorn’s arguments here quite convincing. They are implied in Lenzi’s analysis as well, even though he follows more closely what took place within the written tradition in the first millennium itself.
Lenzi’s approach is to give evidence from the sources to what he labels “the mythology of scribal tradition.”
Helge Kvanvig, Primeval History: Babylonian, Biblical, and Enochic: An Intertextual Reading, Brill, 2011, pp. 151-2.