Asherah, Astarte, Anat, Athirat in Ancient Ugarit
“Some scholars have suggested that El’s two wives in The Birth of the Gracious Gods (Manfred Dietrich, Oswald Loretz, and Joaquín Sanmartín, Cuneiform Alphabetic Texts from Ugarit, Ras Ibn Hani and Other Places (CAT), KTU 2d enlarged edition. Münster: Ugarit-Verlag, 1995, p. 1.23) are mortal women, since they are referred to as ‘attm, “two women.” But it is just as likely that they are goddesses–perhaps Asherah and Rahmay, mentioned prominently earlier in the myth.
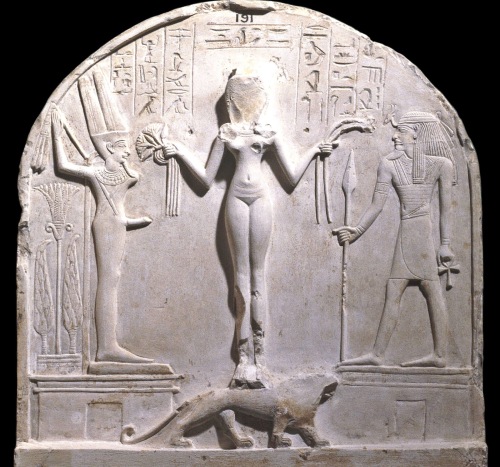

British Museum EA 191, upper register of limestone stele of chief craftsman Qeh. Naked goddess identified as ‘Ke(d)eshet, lady of heaven’ flanked by the ithyphallic Egyptian god Min and Syro-Palestinian god Reshep. Deir el-Medina (Dynasty 19). Photograph © Trustees of the British Museum.
“Her name Qdš(-t) simply means ‘holy’. As such, it can be attached to almost any goddess, including the whole of the A-team: Anat, Astarte, Asherah and Athirat. The question is: did there exist an independent goddess named Qedeshet at all? She is not known from any Canaanite or Ugaritic texts or inscriptions. Rather, she only appears as a named goddess in Egypt. There, she is honoured with such typical titles as ‘Lady of heaven’ and ‘Mistress of all the gods’ — which are not specific to her but could equally apply to any goddess in Egypt.”
http://judithweingarten.blogspot.com/2014_01_01_archive.html
In any case, these women become “El’s wives, El’s wives forever” (CAT 1.23.48-9) and give birth to two gods, Dawn and Dusk. There is much about this myth that is obscure, and nothing substantial that sheds light on Genesis 6:1-4.
In later West Semitic texts, the term “Children of El” (bn ‘ilm) is occasionally used, as at Ugarit, to refer to the main group of gods under the high gods. The Phoenician inscription of King Azitawadda (8th Century BCE) invokes a local sequence of gods: “Baal of heaven, and El the creator of earth, and the eternal Sun, and the whole council of the Children of El (bn ‘lm) (KAI 26. A.iii.19).
A Phoenician inscription from Arslan Tash (7th Century BCE) invokes the “Eternal One” and probably “Asherah,” followed by “All the Children of El (bn ‘lm) and the great of the council of all the Holy Ones” (KAI 27.11-2). An Ammonite inscription from the Amman Citadel (8th Century BCE) exhorts: “[Be]hold, you should trust(?) the Children of El (bn ‘lm).” These brief notices indicate that the term “Sons / Children of El” continued in use in the first millennium with the same general sense as in the second millennium texts.
Some Hellenistic era Phoenician traditions preserved in the writings of Philo of Byblos have been adduced as comparable to the themes and characters in Genesis 6: 1-4 (A.I. Baumgarten, The Phoenician History of Philos of Byblos (Leiden, 1981), pp. 156-7), but their relevance is dubious. In a portion of Philo’s Phoenician History (as quoted by the church father Eusebius), an interesting sequence of primeval history is related:
“From Genos, the son of Aion and Protogonos, there again were born mortal children whose names were Phos, Pur, and Phlox. These–he says–by rubbing sticks together discovered fire, and they taught its use.
And they begot sons who in size and eminence were greater [than their fathers] and whose names were given to the mountain ranges over which they ruled, so that they Kassios, the Lebanon, the Anti-Lebanon, and the Brathys were called after them.
From these–he says–were born Samemroumos who is also [called] Hypsouranios and Ousoos. And–he says–they called themselves after their mothers, since the women of that time united freely with anyone upon whom they chanced.” (Eusebius, Praeparatio evangelica 1.10.9)
These are probably authentic Phoenician traditions, but they have been filtered through Philo’s Hellenistic hermeneutics. If these traditions were about primeval humanity, as the text suggests, then the comparison with Genesis 6:1-4 would be warranted, particularly the birth of giants and perhaps the sexual adventures of women in primeval times. But it has long been clear that the characterization of these figures as human is due to Philo’s Euhemeristic technique, in which the stories of the gods have been transposed into stories about humans.
The clues that this is a sequence of divine figures include the following: Aion (“Eternity”) is identifiable as the well-known Canaanite / Phoenician god ‘Olam (“Eternal One”), as in the Arslan Tash inscription above; the children who discover fire are named “Light,” “Fire,” and “Flame,” also identifiable as Canaanite / Phoenician gods; their sons whose names are given to mountains are identifiable as local Baals—Baal of Kassios (= Mount Zaphon), called Zeus Kassios in Hellenistic times, Baal of Lebanon, and Baal of Anti-Lebanon (= Mount Hermon); Samemroumos means in Phoenician “High Heaven” (= Greek Hypsouranios), perhaps related to Baal of Heaven in the Phoenician inscription of Azitawadda above, or to the temple precinct in Sidon called “high heaven.”
Gold pendant, possibly Astarte. Ugarit. 1500-1200/1150 BCE.
Drawing © Stéphane Beaulieu, after Toorn 1998:86, #31
http://www.matrifocus.com/IMB04/spotlight.htm
The “mothers,” champions of free sex in Philo’s text, are likely to be goddesses, though their identities are unclear. Astarte and Anat (called in a Ugaritic text “Lady of High Heaven”) are good candidates.
Phoenician traditions about gods of mountains and about goddesses who have sex and bear divine offspring are interesting of themselves, but do not bear directly on the story or characters of Genesis 6:1-4. The same lack of connection pertains to stories about open conflict or rebellions among the generations of the gods (related in Philo’s Phoenician History among other sources), since this theme is not perceptible in Genesis 6:1-4.
Nonetheless, the long duration of the “Sons / Children of El” in West Semitic lore indicates that the story in Genesis 6:1-4 is rooted in widespread cultural traditions. But, perhaps because our textual evidence is so sparse, we lack other West Semitic narratives that are clearly related to Genesis 6:1-4.”
Ronald Hendel, “The Nephilim Were on the Earth: Genesis 6:1-4 and its Ancient Near Eastern Context,” in Christoph Auffarth and Loren T. Stuckenbruck, eds., The Fall of the Angels, Brill, 2004, pp. 24-7.
