Kvanvig: Antediluvian Scribes of the gods
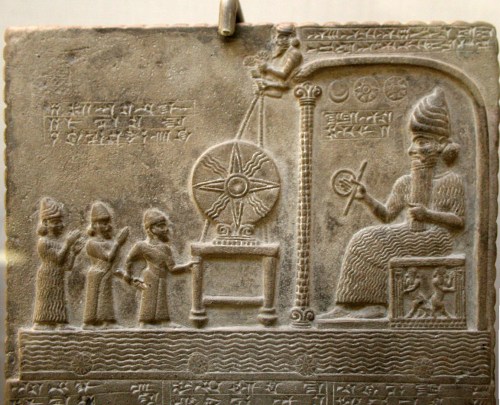
“We find an indication that Uanadapa was regarded as a recipient of revelations, we find it in the Verse Account of Nabonidus, where the king compares himself with Adapa. He boasts of his “wisdom;” he has “seen what is hidden” and “secret things:”
“He would stand in the assembly (and) exalt him[self] (as follows):
“I am wise, I am learned, I have seen what is hidden.
I do not understand the impressions made by a stylus, (but) I have seen se[cret things].
Ilteri has shown me; he has [made known to me] everything.
As for (the series) Moon Crescent of Anu (and) Enlil, which Adapa has compiled,
I surpass it in all wisdo[m].”
(Verse Account of Nabonidus v, 8′-13′).
The text does not claim that Adapa has written Enuma Anu Elil; it states that Adapa had “compiled,” kasāru, the series. This is the same verb that is used about Kabti-ilāni-Marduk in the quotation from the Poem of Erra above; he is kāsir kammīšu, “compiler of his tablets” (V, 42).

Enuma Anu Enlil is a series of about 70 tablets dealing with Babylonian astrology. These accounts were found in the early 19th century by excavation in Nineveh, near present day Bagdad. The bulk of the work is a substantial collection of omens, estimated to number between 6500 and 7000, which interpret a wide variety of celestial and atmospheric phenomena in terms relevant to the king and state. The tablets presumably date back to about 650 BC, but several of the omens may be as old as 1646 BC. Many reports are “astrometeorological” forecasts (Rasmussen 2010).
http://www.climate4you.com/ClimateAndHistory%205000-0%20BC.htm
The reason for this is clear; he did not compose the content of the tablets himself; a god revealed the content to him. What he did was to repeat what was revealed and arrange it on tablets.
The same must be meant with Adapa. He was not the original composer, but the transmitter of Enuma Anu Enlil. The original composer of the series was, according to the Catalogue, Ea himself (cf. A Catalogue I, 1, Cf., Machinist and Tadmor, “Heavenly Wisdom,” p. 147.)
This placement of Adapa in the role of transmitter of divine writings is also attested elsewhere in the Catalogue (VI, 15-6). The second time he is listed in connection with writings, they originate ša lām abūbu, “from before the flood.”

Click to zoom.
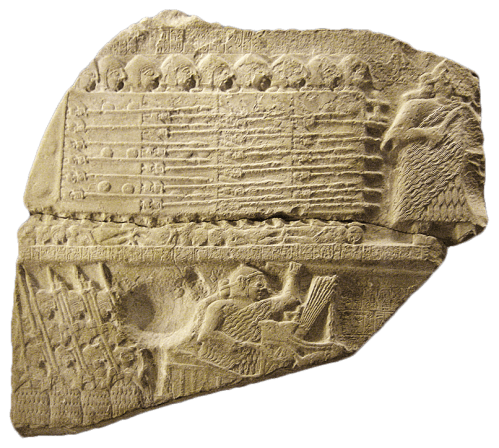
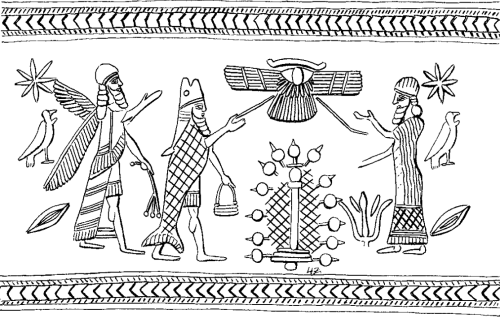
A solid basalt tub recovered from outside the Temple of Ishtar at Nineveh, now in the collection of the Pergamon Museum.
Ea is readily identified at the center with water flowing from his shoulders. Ea is surrounded by apkallu, puradu-fish apkallu.
The puradu-fish apkallu have fish heads and fish bodies draped down their backs. They raise rectangular objects of unknown etiology in their right hands, in their traditional acts of purification and blessing. The banduddu buckets are, as usual, in their lowered left hands.
This tub probably portrays the Seven Sages of antediluvian Sumeria.
The next line shows the circumstances of his composing: [Ada]pa ina pîšu išturu, “Adapa wrote according to his mouth,” i.e. “at his dictation.” Here Adapa is again the second link in the chain of transmission. The compositions from before the flood were dictated to him by a god.
Lambert claimed in his edition of the Catalogue that “the lack of a consistent chronological scheme is striking.” Not all agree with him in this assessment. A. Lenzi has called attention to the fact that the two first authors in the Catalogue are Ea and Uanadapa, starting a chain of scribal transmission.
(Lambert, “A Catalogue,” p. 76; Lenzi, Secrecy and the Gods, p. 119.)
K. van der Toorn has suggested a new interpretation of the text belonging to fragment VI, 15-7 in Lambert’s ordering of fragments.
(K. van der Toorn, Scribal Culture and the Making of the Hebrew Bible, Cambridge, 2007, pp. 207-8.)
While the previous reading has been to see this text simply in the succession of the listed works, van der Toorn assumes that the fragment “is either an explanatory commentary to fragment I, 1(5)-7 or an explanation of the chain of tradition pertinent to all the works previously listed.” He suggests a restoration of the sequence which is intriguing:
[Texts and recipes] from before the Flood
[which Ea spoke and Ada]pa wrote at his dictation
[and which NN] wrote down from the mouth of Anšekurra.
(Catalogue of Texts and Authors VI, 15-7, ibid., note 9, p. 342.)
van der Toorn interprets the last name given here as Sumerian an.še.kur.ra, meaning “he who entered heaven” as an appellation of Adapa. This comports well with what we have observed about the first sage, U-an, “light of heaven” in the Adapa Myth and Bīt Mēseri.”
Helge Kvanvig, Primeval History: Babylonian, Biblical, and Enochic: An Intertextual Reading, Brill, 2011, pp. 148-9.