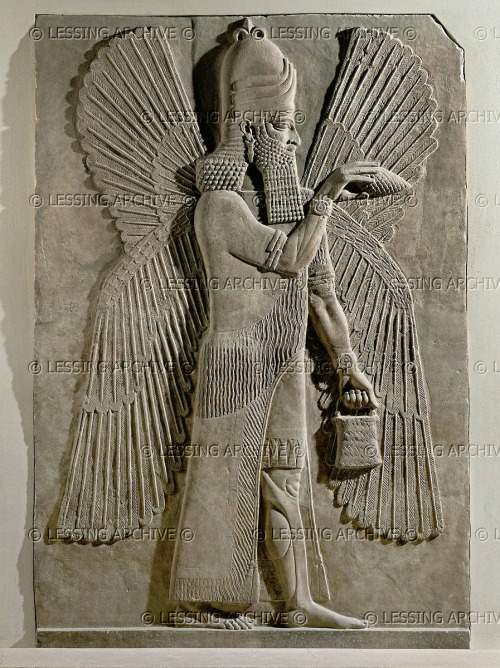
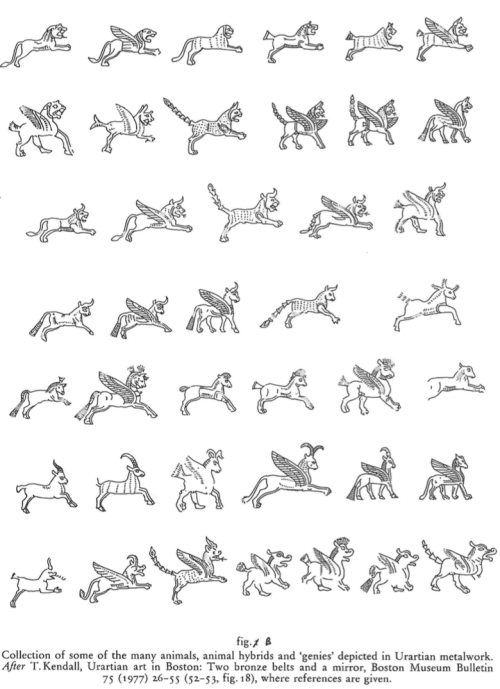
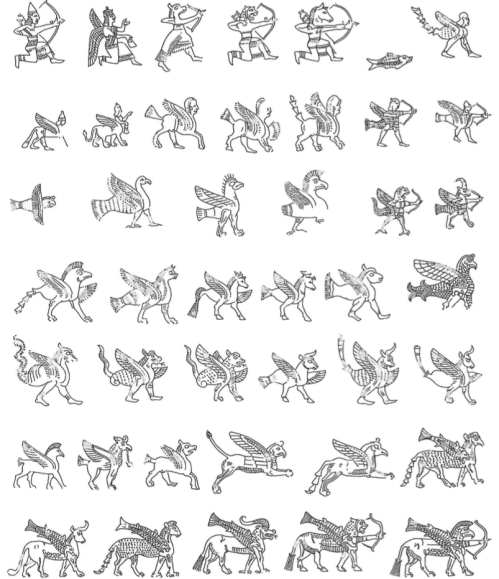
Gane: A Study of Mischwesen in the Neo-Babylonian Period
“This study investigates the contribution of iconographic depictions of composite beings, commonly referred to by the German term Mischwesen, toward an understanding of the worldview of the Neo-Babylonians. This important aspect of their art provides access, albeit limited, to Babylonian ideology.
Unlike previous scholarly treatments of Mesopotamian supernatural hybrids, this study focuses on all extant, provenanced composite beings of a single period.
Focusing on a narrow one-period corpus facilitates the possibility of identifying correlations between emblematic visual elements and evidence for the perspectives of those who produced and viewed them, namely, the Neo-Babylonians.
The Neo-Babylonian Empire lasted from 626 to 539 BC. However, the present cultural research follows Edith Porada’s chronological framework for the iconography of NB material, which begins about 1000 BC and extends just past the fall of the Babylonian Empire in the sixth century BC.
(Edith Porada, “Suggestions for the Classification of Neo-Babylonian Cylinder Seals,” Orientalia 16 (1947): 145-165, pls. III- VIII.)
This study gathers and builds on several branches of previous scholarship, such as publications of examples of NB composite beings that provide the data for this research, general investigations of such depictions over their entire history, textual and lexical sources that elucidate aspects of such beings, and explorations of methodology relevant to interpretation of such emblematic art.
Previous works have exposed a number of key concepts applicable to NB composite beings (see further in “Literature Review” below). Most basic is the function of such portrayals as metaphors for supernatural beings, with hybrid body parts representing various attributes.
Also foundational is the principle that a symbolic depiction should be appropriate to its referent (in this case a supernatural being) and the function of the object on which it is portrayed. Another significant concept is the occultization (sic) of some primordial personalities represented by mixed beings.
Any attempt to draw immutable conclusions in this area of research is fraught with inherent limitations.
First, the extant NB set of data is only a partial representation of all the hybrids produced during this period, and does not include items that have been destroyed, remain undiscovered, or are at least inaccessible to scholars.
In particular, it is important to avoid making arguments from silence.
Second, even if all NB composite beings were available, they did not comprise or belong to a thoroughly unified or consistent system.
(Cf. Jean Bottéro, Religion in Ancient Mesopotamia (trans. Teresa Lavander Fagan; Chicago: University of Chicago Press, 2001), pp. 26-28. A. Leo Oppenheim states, “A systematic presentation of Mesopotamian religion cannot and should not be written” (Ancient Mesopotamia: Portrait of a Dead Civilization [Chicago: University of Chicago Press, 1964], p. 172).
Rather, the NB repertoire of hybrid creatures results from complex accretions over millennia. Therefore, we should be cautious about making generalizations.
Nevertheless, in this study I will explore patterns emerging from the data that will illuminate the place of composite beings in the cosmic community.
This will shed light on the nature of the cosmos and the degree to which its elements are interconnected in the worldview of the Babylonians, as reflected in their iconography.
Constance Ellen Gane, Composite Beings in Neo-Babylonian Art, Doctoral Dissertation, University of California at Berkeley, 2012, pp. 1-2.